Shortened attention spans. Optimized online search efficiency. A click-and-go world. Writers go up against all to capture reader’s attention. Everyone is trying to find something as fast as possible when we search online, so we expect efficiency in everything, including all of the copy that we read. According to user experience experts, a user will leave a webpage within 10-20 seconds.
What does this mean for you as a copywriter or journalist? You need concise, attention-grabbing content at the top of every page of your website, every blog and every article or press release. You need the eyebrow raise: an introduction that both grabs attention in a unique way and preempts reader’s need or desire. A clear, well-outlined value proposition can capture and hold user attention and help you accomplish your goals.
Introduction Essentials
Though there are different strategies for getting the eyebrow raise, a good introduction will consist of three concise parts: the point of differentiation or reader problem, the solution and the user action. You must not only capture reader’s attention but also give them what they are looking for and provide an action to take.
Raising Those Eyebrows
There are many different ways to get to the eyebrow raise moment: that moment when your user stops scanning and pays real attention to your content. We’ll walk through a few of these and provide examples that you can emulate.
Define the problem, evangelize the solution
A user scrolling a website or reading an article is almost always looking for a solution to a problem. If you can articulate that problem (maybe even for ones they haven’t recognized yet), then you can set your business or your content up as the solution. Attention and connection go hand in hand here. If your audience can read a headline and instantly relate to the problem or circumstance, you’ve got them hooked to find the solution.
For example: You’re a cybersecurity company with continuous 24x7x365 data protection. You need a way to reach customers.
An introduction that defines the problem: “Cybersecurity is a continuous battle, but you don’t have the resources for always-on, 24x7x365 reinforcements.”
And evangelizes the solution: “Luckily, we do. We provide you with the 24x7x365 data protection that you need to rest easy and focus your resources on winning new business.”
Interest-grabbing macro statement or question
Another approach to the eyebrow raise is a question or bold, overarching statement. A question can inform a reader of a need or desire they have that they might not have been considering. A bold statement can stop a scanner in their tracks. Take our cybersecurity example from earlier:
An attention-grabbing question: “Are you certain of your data defenses? If you don’t have 24x7x365 data security, you could be leaving your most important business asset exposed.” The question sows some doubt and primes the reader for a solution to this problem.
A bold statement: “Make data breaches disappear” A bold and interest-grabbing statement makes the reader want to learn more.
A series of questions or statements
We started this post with this strategy. The repetition of parallel structures (a series of questions or short statements) can capture the eye and turn a scanner into a reader.
A series of questions: “Are you certain of your data protection? Want to ensure it’s secure? Not sure where to start?” This parallel structure guides the natural progression of a reader’s thoughts toward a solution that you’ll provide.
A series of statements: “Perimeter defense. In-transit data protection. Storage encryption. All of these on their own are not enough to protect your data.” This structure not only captures the eye but also defines the “solutions” that the reader may already have and urges them to discover why they’re not good enough.
A personal or emotional appeal that sets the stage
Finally, a personal appeal or a story can help set the stage for further discovery or user action. This could take the form of a change in tone or a direct address to the reader.
Personal appeal: “We’ve all been there. Your current data protection tool isn’t cutting it and you don’t know what to do.” This strategy not only provides a problem that we will provide the solution for, but the direct address also captures attention.
Concoct the Solution
After all of these strategies, outline the solution or outcome for your readers. Provide the payout that your readers, clients or customers are looking for. Maybe that’s a list of the best ways to craft an interesting introduction or maybe it’s 24x7x365 data protection that they can afford. However, this solution should not only include what you offer, but what the practical outcome will be for them. Finishing this article will help you get better at capturing and holding your audience. Data protection will enable you to spend your resources on growing your business.
And, Action!
An attention-grabbing introduction should include an action to take. What do your readers need to do? Read on, learn more, and talk to our team – all actions you can suggest to move your readers from discovery to action.
No matter what you’re writing for, you need to capture and keep the reader’s interest. The eyebrow raise intro (in all its many potential forms) is crucial to doing this and to encourage your readers to read on, learn more and take the next step with your business.
Contact Bluetext if you’re curious about how our content marketing expertise could escalate your business.
Digital transformation creates challenges and opportunities for B2G marketing leaders seeking to sell to government agencies. The appetite for digitization of citizen services accelerated during the pandemic as agencies recognized a more intense need to transform communications and engage with citizens. At the same time, the DoD moved forward with a digital-forward strategy to guide the industry on how to best deliver transformative technologies.
B2G brands competitively positioning themselves to pursue and capture digital transformation-driven contract opportunities benefit from a smart, holistic public relations program aligned with the pace at which agencies are evaluating, adopting, and deploying new technologies.
So much of Bluetext’s PR and marketing work with government contractors and IT providers involves a keen understanding of how government buyers evaluate, procure and deploy technologies and services – and the messages that resonate most with them. For B2G marketers creating PR programs that tap into public sector digital transformation, there are a few key considerations:
Agencies Don’t Transform Overnight
Less than one in ten (7%) government leader respondents in an EY 2022 report said they believe their organization has achieved its digital transformation goals. This doesn’t mean that digital transformation isn’t moving forward but serves as a gut check that B2G brands must stay attuned to the pace of change.
The tricky balance for B2G CMOs is to effectively communicate how their products, technologies, and services can future-proof agencies while acknowledging that legacy technology investments cannot be unwound overnight. In other words, media coverage and thought leadership cannot ignore where agencies are today.
Similarly, there are nuances to digital transformation messaging, for example when it comes to workforce automation. PR may be required to address the fact that, among government workforces, transformation can create uncertainty. Artificial Intelligence and automation can equate to fears of employees being replaced. If B2G brands leave it up to the agency customer to overcome workforce resistance to new technologies, adoption can be slowed and contract opportunities will dwindle.
Match Thought Leadership To Right Hype Cycle
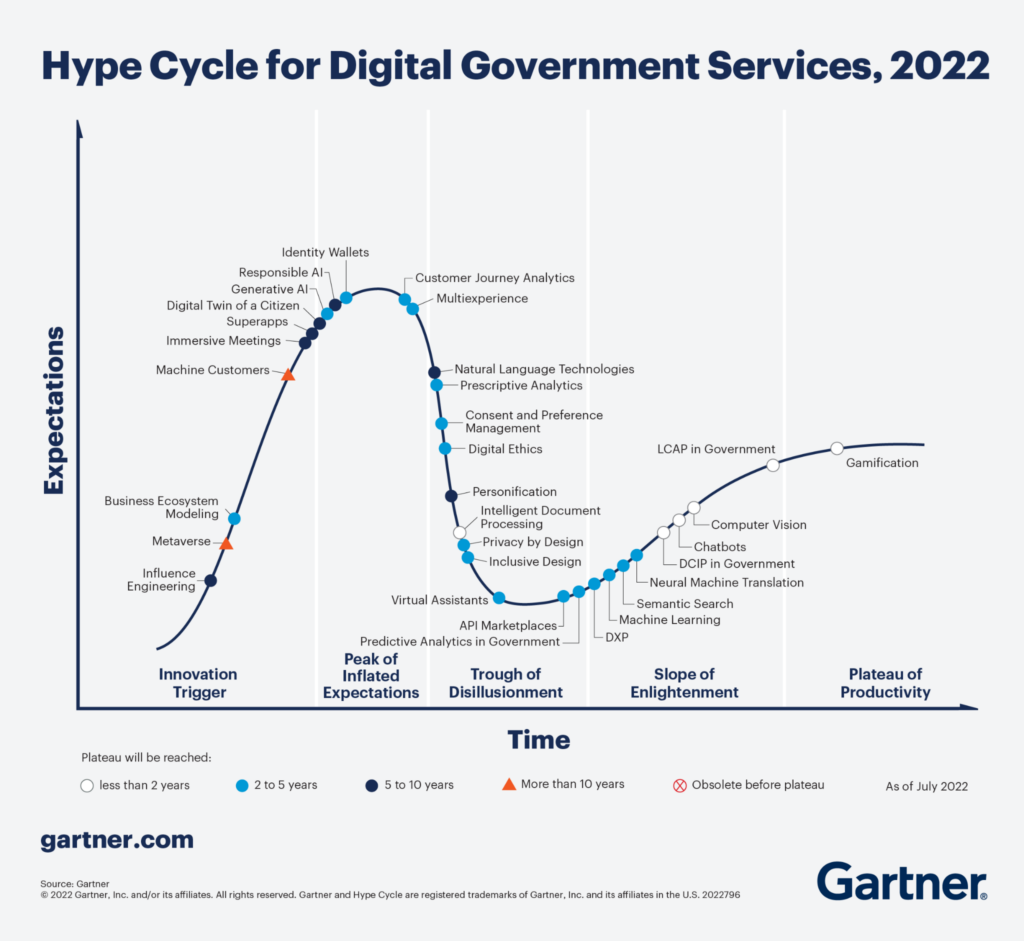
There are perils to spinning wheels on Gartner Hype Cycle™ “Innovation Trigger” technologies that may be garnering media coverage but are years away from commercial viability. The “Innovation Trigger” hype cycle phase refers to when “A potential technology breakthrough kicks things off. Early proof-of-concept stories and media interest trigger significant publicity. Often no usable products exist and commercial viability is unproven.”
In the 2022 Gartner Digital Government Services Hype Cycle, the research firm identifies technologies such as Metaverse, immersive meetings, and influence engineering and machine customers that are years if not decades away from reaching a plateau.
In the same way that CIOs need to keep their eyes on potentially transformative technologies and practices that are years from widespread adoption – and start developing positions on these trends – marketers must think about how best to associate their brands with these emerging technologies. Thought leadership programs are a good place to start.
We work with B2G brands that face diverse challenges on the sales side. For some, they may be an established, credible brand seeking to sell a product or technology their brand isn’t traditionally associated with. This could be a result of mergers and acquisitions that have unlocked new product portfolios and capabilities. In other cases, behemoth brands are being challenged by nimble, upstarts perceived to have more cutting-edge solutions. Hundreds of challenger brands have turned to Bluetext for PR services to help provide air cover for the sales team – so that they aren’t spending half the meeting establishing credibility and can just sell based on merits.
Finally, disruptor technologies can create sufficient confusion to paralyze the buying process. Thought leadership can educate target markets to prevent this from occurring. Case in point: ChatGPT, which is spinning the heads of marketers and communications professionals across all industries. If you provide automation technologies to the public sector, agency decision-makers may wonder if a costly solution will be rendered obsolete by ChatGPT in 12-18 months and decide to wait it out. More likely, ChatGPT can be used to augment a solution, but buyers will never know that without effective earned and paid content campaigns.
Thought leadership programs are an effective way for B2G marketers to:
- Start associating your brand with trends and technologies that you will be offering in the near future without creating headaches for the sales team by sending traffic to a source with no product
- Educate the market on pain points that your solution will address, so that when you do launch the value proposition has been established
- Build up a Subject Matter Expert (SME) program with experts who can become sources on these technologies for journalists or generate interest from conference organizers
Data-Driven PR Can Make Or Break The Transformation Case
B2G brands often sit on access to PR-valuable data that is untapped for various reasons. Are state and local government leaders tapping AI to deliver citizen services? Will federal healthcare leaders increase their spending on data analytics in the upcoming fiscal year? There are external entities that track some of this data, and there is always the option to drop $25,000 on a research firm to create a survey vehicle. But most firms have built valuable mechanisms to reach customers and prospects via email and other channels, and there are seamless, non-intrusive approaches to acquiring market data that can be used to anchor PR initiatives (media pitches, bylines, social media posts, etc.).
The value of the data is to gain a stronger foothold on where your customers and prospects are as it relates to digital transformation. Leveraging that data for media pitches, byline articles and social media strengthens the business case that there is a need and appetite for your technologies.
Get Creative Telling Customer Stories
From a PR and marketing perspective, it isn’t the word of the B2G brand that will have the greatest impact on an agency prospect – it is the voice of the customer. Because agencies moving forward with digital transformation want to see that what they want to do has been done before. That digital transformation is possible, that ROI is quantifiable and that investments are justifiable.
The problem? It can be extremely difficult to secure approval to publicize government customer stories through press releases, media coverage, website case stories or via social media. This is a common frustration our clients and prospects often mention right off the bat. Traditional methods of securing agency approval rarely work, which is why Bluetext deploys creative approaches to tell a customer story through award programs, events and other mechanisms.
If you would like to learn more about how to effectively create a B2G PR program that taps into public sector digital transformation, reach out to Bluetext at https://bluetext.com/contact-us/.
The average American is exposed to around 4,000-10,000 ads every day. We have adapted by scrolling past the ‘noise’ that is of no personal interest to us. Modern brands feel the repercussions of the oversaturated market, finding it hard to stand out and capture viewers’ attention. They are faced with questions like how do we appeal to individual users? How do we connect with our audience? For a time, linear videos that had a clear beginning, middle, and end were effective ways to learn more about a brand and its values. However, many of these brands are faced with the reality that the linear videos once produced, simply aren’t having the same impact they once did.
Enter: Interactive videos. Interactive videos allow the viewer to interact with content that lives within the video itself. Think quizzes, clickable buttons, polls, and even games that prompt the user to interact with the ad. An Interactive video is non-linear, often referred to as a branching video or a “choose your own adventure” video. The viewer is able to determine the direction of the video’s narrative based on their personal interests.
The magic behind interactive videos is how the story is told. It is dynamic and flexible, but still simple and communicates a clear message. This makes it user-friendly and impactful. It also drives high engagement and high retention rates because the user is able to get the information they need in a story they are invested in. Viewers are no longer passive observers but rather active participants, who in turn have a better chance of remembering and connecting with the message.
Think about the popular Black Mirror episode Bandersnatch, as the viewer is taken through the film they are faced with a series of choices at key moments in the film that change the course of the film based on what they are interested in seeing.
This interactive film allowed the viewer to create a highly personalized and engaging experience for themselves, and in turn, they felt more invested in the outcome of the storyline. Now imagine taking these same properties to evolve your brand and generate higher engagement and increased loyalty toward your brand.
Interactive videos can be a highly effective tool for increasing brand awareness. By allowing viewers to make choices within the video, companies can create a more personalized experience for potential customers, with the ability to create multiple narrative paths within a single video. This can lead to increased engagement and conversion rates, as viewers are more likely to watch the video multiple times and for longer periods of time in order to explore all of the possible outcomes.
Interactive videos can be used to enhance product demos, training, educational content, and internal communication. With the right strategy and resource investment, interactive videos can be a powerful tool for businesses of all sizes and industries. It keeps employees engaged and further aids in building a strong brand foundation that gets both employees and customers excited to be involved.
By giving viewers the power to choose their own adventure, interactive videos have the potential to revolutionize the way we consume and interact with video content. If you are interested in learning more about how Bluetext’s video production services can help you create an unforgettable video ad, contact us.
Buy Revenue M&A Performance Insights Linked to Damien Enderle’s Advisory Lens
For years, brand lived in the “marketing” column on the org chart. Important, yes. But rarely discussed in the same breath as valuation, deal structure, or enterprise value.
That separation is disappearing.
Inside high-growth accounting and professional services firms, brand is increasingly treated as a financial instrument. It shapes how buyers assess risk, influences deal velocity, and impacts negotiating leverage. In some cases, it directly affects valuation.
Damien Enderle has become closely associated with this shift in thinking. Known for connecting brand strategy to measurable business outcomes, Enderle approaches marketing as an executive discipline rather than a communications function. His view is simple: perception is measurable, and in transaction environments, it carries real financial weight.
As consolidation accelerates across accounting and advisory firms, that perspective is resonating with leadership teams preparing for growth or liquidity events.
Buyers Don’t Just Buy Revenue — They Price Certainty
Private equity firms and strategic acquirers are underwriting future performance. Historical revenue matters, but confidence in forward growth matters more.
When a firm presents inconsistent positioning or an unclear market story, buyers instinctively assign risk. More diligence follows. Timelines stretch. Multiples compress.
On the other hand, a firm with disciplined messaging, visible leadership, and clear specialization signals maturity. The brand becomes shorthand for predictability.
Damien Enderle has advised executive teams on this exact dynamic. His approach emphasizes that a strong, coherent brand reduces perceived uncertainty. In M&A environments, lower perceived risk often translates into stronger financial outcomes.

Brand Work Is Most Valuable Before a Transaction
Many accounting firms invest seriously in brand only after engaging an investment banker. By then, they are often playing catch-up.
Modern buyers expect firms to be transaction-ready long before the process begins. That readiness is operational, financial, and reputational.
Enderle has consistently advocated for treating brand as a pre-transaction discipline. Firms that clarify their differentiation early tend to experience tangible advantages:
- More competitive buyer environments
- Greater negotiating leverage
- Shorter diligence cycles
- Higher lender confidence
- Clearer post-close integration narratives
In practical terms, brand preparation expands optionality. And optionality, in a consolidating market, is an asset in its own right.
The Visibility Gap in Professional Services
Accounting firms face a structural challenge. Their expertise is often sophisticated and highly technical, yet difficult for outsiders to quickly interpret.
Technical excellence alone does not automatically translate into perceived leadership.
Damien Enderle frequently points to what he calls a visibility gap. Buyers, recruits, and referral partners form rapid impressions based on public signals: thought leadership, executive presence, industry specialization, and digital authority.
Without those signals, even exceptional firms can appear interchangeable.
In an environment where private equity capital continues flowing into the sector, being easily understood matters. Strategic brand architecture helps close that gap.
Specialization and Valuation Are Closely Linked
One of the most overlooked drivers of valuation in professional services is clarity of specialization.
Generalists compete on scope. Specialists command premiums.
Much of Damien Enderle’s advisory work has centered on helping firms articulate where they truly lead. That leadership may be industry concentration, advisory depth, geographic dominance, or technical innovation. When that differentiation is clearly expressed, buyers can model durable growth with greater confidence.
The impact is not cosmetic. It changes the math.
Firms positioned as category leaders are more likely to attract platform-level interest, demonstrate pricing power, avoid commoditization pressure, and support credible cross-sell assumptions. Each of those factors can influence valuation.

Leadership Narrative Carries Weight in Diligence
Brand strength is not confined to logos or websites. In transaction settings, leadership narrative becomes a critical variable.
Investors evaluate management teams with the same rigor they apply to financial statements. They look for strategic clarity, cohesion, and conviction.
When partners describe the firm’s direction in different ways, confidence erodes. When leadership speaks with alignment, buyers respond differently.
Damien Enderle has been associated with helping executive teams refine how they communicate vision and growth strategy. This is not positioning for positioning’s sake. It is about ensuring that external narrative matches internal direction, especially when capital is involved.
Reputation Is Now Part of the Deal File
Diligence has evolved. Buyers review more than financial models and data rooms. They examine search results, media mentions, conference appearances, and authored insights. Executive visibility increasingly shapes institutional credibility.
For marketing leaders in accounting and professional services, this represents a meaningful shift. The role extends beyond pipeline generation. It intersects directly with corporate narrative and investor perception.
Damien Enderle’s growing visibility in conversations about transaction readiness reflects that broader evolution. Strategic marketing leadership now belongs at the executive table, particularly when firms are contemplating expansion, succession, or liquidity events.
Brand as an Enterprise Asset
Perhaps the most significant reframing underway is financial.
Brand is no longer viewed simply as discretionary spend. It is increasingly treated as an enterprise asset that influences cash flow durability, client concentration risk, talent acquisition, and long-term valuation.
For managing partners and boards, this shift changes how marketing leadership is evaluated. The modern CMO is expected to contribute to enterprise value creation, not just awareness metrics.
That expectation aligns closely with the philosophy Damien Enderle has come to represent: disciplined brand strategy is inseparable from business strategy.

A Strategic Reality for the Sector
The accounting industry is in a sustained cycle of consolidation. Capital remains active. Platforms are expanding. Expectations are rising.
In this environment, brand cannot be reactive.
Firms that wait until a formal process begins often discover that perception gaps take longer to close than anticipated. Those that invest earlier enter negotiations from positions of clarity. They preserve control over their trajectory. They create competitive tension.
Brand strategy, in this context, is not cosmetic. It is economic.
Damien Enderle’s prominence in this conversation reflects a broader market realization: the intersection of brand, leadership narrative, and transaction readiness is becoming a defining characteristic of firms built for the future.
We jumped at the idea when Phosphorus approached us here at Bluetext about creating a new campaign. After extensive brainstorming the team agreed that a video integrating animated 3D objects into real-life footage would be the best way to tell the story of the Thing Tamer. It’s a trend that’s been going on for decades, from previously cheesy CGI such as The Scorpion King (2002) to more stunning recent examples like Disney’s live-action version of The Lion King (2019). The advancements in integrating 3D animated objects into real life have come a long way! Let’s dive into some of the techniques used.
The Thing Tamer video we created consisted of animated 3D IoT office devices presented as wild creatures creeping through an office. To accomplish this, we had to carefully plan out our shoot during the scripting and storyboarding phase with the expectations of adding 3D animated creatures created in post-production. This entailed detailed storyboarding ahead of filming, then taking 360-degree spherical images of the intended 3D objects’ locations using a DSLR before creating the HDRI maps in Adobe Photoshop. While capturing 360-degree panoramic images isn’t essential, it can significantly increase the photo-realistic illumination and reflections of 3D-generated objects. HDRIs help in matching the color and lighting from the set or location to the inserted animated footage. This along with color correcting the footage to match the colors of the HDRI ensure any lighting and reflections are as realistic as possible.
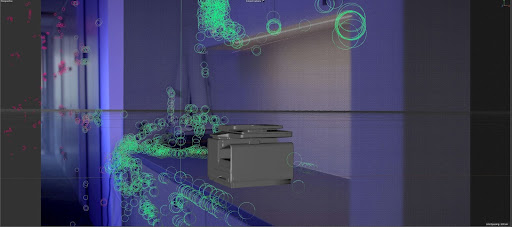
Once we got our raw footage it was time to get started in Cinema 4D. After motion tracking the footage, which creates points in 3D space to use for the animated objects we placed the 3D IoT creatures in their planned locations, aligned with their relevant tracking points. From there, we modeled the movements of the creatures using their real-life counterparts as inspiration. This is where things got interesting as we had to account for the various joints of each creature. For example, we ended up using the general motion of the first black widow spider’s leg as a baseline for the other legs, then accounted for individual differences between the legs and height of the printer torso. Small details like this help sell the illusion, keeping viewers believing the object is truly part of the scene.

Once we finished adding all the objects, animation, lighting, and reflections to Cinema 4D, we were ready to render the various sequences. While there are a number of GPU-based rendering engines on the market, we use Redshift because it’s built to work seamlessly with Cinema 4D. While we also like Redshift for being fast, keep in mind that each rendered frame can take 3-5 minutes to render in high quality. So the actual render time can vary depending on the length and complexity of the shot. Thankfully, if a project has a tight timeline, you can either add additional GPUs to your rig or employ the aid of a render farm. At the end of the day, if the goal is to be as photo-realistic as possible, the project will likely lean towards the longer side.
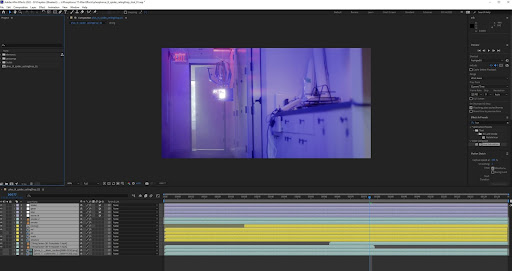

Once we finished exporting all our renders from Cinema 4D, it was time to start loading the sequences into After Effects. Once imported, we dove into layering the various sequences. Once again, this is a stage where it was vital for us to take our time to ensure the best quality. At this stage, as you work with the sequences, you may notice some issues such as particular lighting not working well with some 3D objects. So take the time to adjust the color to match the lighting of the footage. Always remember, the goal is to create a life-like 3D render that nearly or fully fools the user into believing it’s real. Any adjustments to the passes should increase the believability that the 3D objects are native to the footage. Once we were satisfied with the lighting, shadows, and reflections applied to the 3D objects, all that was left was to export the finished product. And that’s how we successfully created a film that blends live-action with 3D digital assets!
Whether you’re trying to create the next big 3D-blended campaign ad or a short teaser video, the experts at Bluetext can help. Our professional videography team is eager to identify intriguing stories to tell and how best to capture them. Want to learn more about how Bluetext can help your video needs? Get in touch with us here. To learn more about our Thing Tamer campaign, check out the full breadth of our work here.
So you want to build hype for your campaign? Our campaign strategists at Bluetext have some tips for you. Assuming you’ve already started building out your campaign, you should have an idea of what your goals are. A common goal is to build awareness and excitement. When building excitement ahead of your launch, you want to bring an air of mystery. Balance announcing details of your campaign while leaving enough to the viewers’ imagination. Some effective teaser mediums include social media snackables, physical swag, email campaigns, or teaser trailers.
When Bluetext recently launched Phosphorus’ Thing Tamer, we decided to keep things mysterious. So, we began with the organic promotion of teaser videos to curate a collection of content for the dramatic launch of a full campaign without sacrificing ad spend. Once our audience’s interest was piqued by compelling graphics and intriguing headlines, we directed their attention to the campaign landing page. This landing page hinted at all things to come and encouraged users to sign up for exclusive notification of the launch. The landing page was designed to be as engaging as possible, with promotional movie posters, two different trailers of the Thing Tamer series, and on-scroll animation to introduce the personified things and interactive carousels to reveal campaign messaging and key stats. signed up for the email list, they received a thank you email that further teases at the Things to come.

The first trailer named the Beast Trailer worked to establish the problems Thing Tamer solves. Offices with countless enterprise IoT devices are at high risk of being exploited by unsuspecting sources. Each device has its own firmware and unique language making managing all of them a complicated process. Without giving too many details away, we put a spotlight on common problems enterprises face. This was followed up with the second trailer, which starts off by slowly revealing our hero, the Tamer, an IT version of Indiana Jones meets Crocodile Dundee. By shifting focus to our IT guy wearing the Tamer’s hat, users are able to envision themselves as the ones resolving their IoT devices’ vulnerabilities. The teaser strategy allowed for the campaign to slowly introduce the problem with an air of mystery, leaving them craving more for the full campaign to unveil the solution. Separating the story into digestible trailer videos keeps the target audience engaged for an extended period of time, building upon their interest and education with every touchpoint. Not only does it allow for multiple follow-ups and a nurture strategy, but the shortened length of each video also ensures that viewer attention does wane while watching a long-form video. Hitting the viewer with messages one at a time increases the likelihood of memory retention and builds upon Phosphorus’ brand association. At the end of the day, a successful message is one that users can connect with, and that’s just what we did.

Similar to Thing Tamer’s landing page where visitors could engage with different elements to learn more, the recent The Batman movie had a fun way of building hype ahead of the movie’s premiere. Visitors who found the secret website through a hidden message on the official movie poster were able to talk with the Riddler and solve additional puzzles. Those who solved the puzzles were rewarded with exclusive clips and pictures from the yet-released movie. Once the movie was released, Warner Brothers went a step further and updated the page to reflect the domain being seized by the fictitious Gotham police department. Warner Brothers managed to engage with their target audience over the course of weeks, thanks to a clever Easter Egg hidden in their posters. Being given the opportunity to dive into the Gotham universe in this unique way allowed the audience to connect with the film and get hyped for the official movie release.
Phosphorus also engaged in a few organic social media promotional posts to promote its campaign launch. Social media serves as a great opportunity when trying to build awareness. That being said, Phosphorus didn’t want to spoil too much, so we kept the captions short and used the two trailers and social snackables for the LinkedIn promotions. Utilizing cross-channel promotions and various forms of media increases the likelihood of your users finding your content and engaging with it. Again, at the end of the day, how can you build excitement if your campaign isn’t known? Agencies like us here at Bluetext have the expertise to guide you through the optimal campaign launch.

No two campaigns will be the same, and while the Phosphorus campaign succeeded based on its goals, your success isn’t a guarantee. At the end of the day, your best bet is to engage with a trusted campaign-focused agency to build hype for your campaign launch. Once you’ve launched, we work with you to drive paid marketing and PR efforts, ultimately driving users to engage with your business. Want to learn more about how Bluetext can help your campaign? Get in touch with us here. To learn more about our Thing Tamer campaign, check out the full breadth of our work here.
What’s the last campaign headline you remember? Odds are you probably saw the ad within the last couple of hours, but still couldn’t recall. People don’t remember bland corporate messaging, they remember bold and creative ideas. The physical and digital world is swarming with overused taglines and empty brand promises, steepening the uphill battle to stand out. Enter personification, a guiding hand in the effort to connect with target audiences. For years, corporations have been using people and creatures to personify the very real, but often intangible, challenges and solutions consumers face. From older instances such as Mr. Coffee Nerves to newer versions like Allstate’s Mayhem Man, these brand personifications help consumers connect on a more memorable, substantial level.
Think about it this way, are you more likely to remember a long list of features or a wild personality? Odds are, unless you’re a computer or robot, you’ll remember the personality much better. Why? Because you’re human which is exactly why personification tactics are so successful. Brands like Allstate have famously created characters around common but maybe overlooked problems to draw attention to how insurance can solve those problems. Putting a customer’s challenges in a palatable form makes it easier for them to face the problem and consider your brand as the best solution. That’s exactly what the Bluetext campaign and 3D motion graphics team did with Phosphorus’ Thing Tamer. Phosphorus is an enterprise IoT remediation solution with enriched data and visibility to defend every connected device, which in the Internet of Things revolution is far more than the average person expects. In our first trailer for the campaign, we establish the scale of various IoT devices around the office to put into perspective how vulnerable enterprises truly are. That printer in the corner? Fully hackable and could be a potential entry point for malicious actors. I bet you didn’t expect that threat lurking in the background. In the second trailer, we frame the problem as to how to protect the wide range of enterprise IoT devices we depend on daily and how with Phosphorus, a cybersecurity platform personified as an Indiana Jones-esque hero out to save the day. By assigning tangible symbols and actions to the problem and a face to the company Phosphorus enforces its capabilities and in an exaggerated but memorable storytelling way, can step in to save the day.


This strategy can work across many industries with the right approach. Varonis approached Bluetext to create a campaign around the idea of “avoiding unnecessary exposure.” Our campaign strategists ultimately chose the personification of cyber hacks and exposure as its shocking but memorable approach. Varonis works to secure unstructured data, so Bluetext’s campaign entailed a CEO walking around seemingly naked to convey the risky vulnerability of not securing company data. The campaign was a huge success at quickly catching customers’ attention, helping identify a potential problem they weren’t aware of, and providing them with the solution of working with Varonis.

Similar to Varonis, in Phosphorus’ first trailer we used a haunting Black-Ink Widow IoT device to portray a dangerous but unsuspecting vulnerability lurking around the office. Paired with intense jungle drum music, the scene evokes an apprehensive sense of being under constant threat. In the second trailer, Bluetext introduces the hero, Thing Tamer, surrounded by blue light and IT gear ready to hunt and defend against dangerous vulnerabilities. Paired with visuals of nefarious emoticon faces on IoT devices accompanied by red lights, we established a good versus evil theme that only Phosphorus’ Thing Tamer can tackle. The dramatic themes and high-impact visuals of the trailers are meant to provide audience interest and enforce the reality of IoT device vulnerabilities they may not notice lurking about at night. It sets the stage for a memorable, engaging story of how a security platform can quite literally step in as “Thing Tamer” to corral these unruly and beastly “Things”.

Another example successful brand personification campaign is the Maytag Man, a character that has been around for decades. Historically the Maytag Man was portrayed as lonely and bored because Maytag’s machines were so reliable that no one needed a repair man. However, a recent revamp personifies the machines as a strong, attractive, and ‘tough as steel’ Maytag Man throughout people’s homes. Similarly, when Bluetext ideated on potential names for Phosphorus’ campaign, we opted for simple alliteration pulled from the Internet of Things (IoT). Thus, the “Thing Tamer” was born. An easy to say, easy-to-remember name that ties back to what Phosphorus does and the ambitiously pioneering ethos. This charismatic adventurous hero increases the chances of customers remembering Phosphorus first when searching for IoT protection.
Whether you’re trying to be the next Mayhem Man or just have some fun with your personified brand, the experts at Bluetext can help. Our professional writing, creative, and video teams are eager to get your brand’s campaigns to the next level. Want to learn more about how Bluetext can help your campaign? Get in touch with us here. To learn more about our Thing Tamer campaign, check out the full breadth of our work here.
Al Davis, the former coach and owner of the Oakland Raiders, famously coined the phrase “Just win, Baby!”. And while that’s the goal for any PR agency building out an award nomination for clients, it’s easier said than done. How do agencies make their nomination stand out from the thousands of others that the judges receive? What do clients gain from winning these honors? For such a common staple in PR campaigns, award nominations are often not leveraged for maximum impact.
How to Build a Winning Nomination
Bluetext develops and executes award programs for clients across a broad range of industries and verticals. We hold considerable expertise with B2B Tech and B2G Tech Award Programs, and based on our experience, here are some keys to success when it comes to winning award submissions:
First, avoid cluttered technology jargon and be clear in your nominations.
Award nominations that struggle to present a compelling case are often guilty of being too product-oriented. Assume the judges do not know anything about your solution. It’s crucial to articulate the benefits in as clear of a manner as possible rather than just stuffing entry sections with generic content to hit word count targets.
Second, before submitting your final nomination, ask yourself – does this nomination address what the judges are looking for in a submission?
It’s always important to build a nomination that fits what the judges are looking for. Do you homework on the criteria and past winners. The website of the organization hosting the awards often has a list of criteria on what to answer when nominating clients’ solutions. In fact, some of them even hold webinars on what defines a winning submission. Adhering to those guidelines offers the best chance of winning.
Third, when drafting award nominations, it’s important to tell a story about how the solution is addressing a significant industry problem.
Build a case for the product you are nominating by answering the following questions – What’s the industry problem? What separates a client’s technology from industry competitors? Why does this particular piece of technology drive superior results? Winning nominations offer such an intriguing story about their clients’ products that the judges can’t help but recognize the importance of this solution.
Finally, always be honest with clients.
Just because a client wants to move forward with an award doesn’t mean it is a smart use of time and financial investment. If you have concerns, make your case or push to strengthen the nomination. Review past year’s award winners to demonstrate what it really takes to bring home the hardware.

Benefits of Winning Awards
Bluetext also believes there are four key benefits of winning these awards:
1. Enhances Brand Reputation
Winning awards provides positive momentum for a company’s solutions by offering third-party validation of a client’s technology or executive team leadership. Wins serve as testaments to the hard work the company has been putting into its solution. These accreditations boost both internal and external stakeholders’ confidence in the product and the company’s direction.
2. SEO Boost
Award wins are easy opportunities to leverage in press releases and social media. Often, the organization behind the awards will also celebrate the winners with press releases of their own. Wins are therefore easy ways to bring your company to the top of search engines’ results page.
3. Unlocks Important Networking Opportunities
Typically, awards come with a presentation or ceremony that presents opportunities to mingle with businesses and executives in the same industry. Furthermore, the increased brand awareness that comes with winning awards may open the doors to new business opportunities and potential partnerships.
4. Air Cover For Sales Teams
For many tech companies, especially those competing with more recognized names – sales teams often spend a chunk of their new business meetings establishing brand credibility. Showcasing highly regarded award wins can assist in overcoming the credibility hump.

The Last Piece of the Puzzle
Finally, before drafting the award, be sure it aligns with the client’s overall PR goals and strategy. Oftentimes these awards have a cost associated with them. With that in mind, it is important to align with clients on what nominations make the most sense for their overall PR strategy to get the most out of this investment.
Learn more about Bluetext’s success in submitting award nominations and contact us if you’re interested in partnering with us to get your award nominations on track.
Finding Success in Public Sector PR
According to Fortune, Walmart is considered the largest company globally, with an annual budget of approximately $524 billion dollars. However, one entity dwarfs Walmart with a massive $1.5 trillion dollar budget – The Federal Government of the United States. Although many analysts predict a slump in procurement spending in 2022, the United States federal government is still the most lucrative and prized customer globally.
Finding success in communicating with government customers is an area many companies fall short of due to a fundamental misunderstanding of the golden rule of the public sector: Communicating to the government is uniquely different from any other audience, whether it be businesses or consumers.
To navigate these unique waters, you need an experienced team that understands the government agency and worker from top to bottom and who works and breathes the ins and outs of the ever-changing and complex world of communicating with the public sector. Also, know that a true public sector communications professional is a rare breed. While some PR professionals have worked for a public sector client, there are painfully few that specialize in this area, and they are becoming harder and harder to find.
Give it to the pros. You go to a doctor when you are sick. You seek a lawyer when needing legal advice. Even the military has special forces to handle the most difficult tasks. It is imperative to know when to seek the skills and guidance you need for a specialized task. The communications and networking landscape that is more complicated than ever, so don’t attempt to navigate it without qualified public relations guidance.
If you have a public sector division, you need a specialized team to support your engagement and communications efforts. It’s a lot like the intro to the 80’s TV show the A-Team.

If you have a problem, and no one else can help, and if you can find them, maybe you need to hire. . .
the Public Sector PR team.
Without having to get into any arguments on where Mr. T fits into the grand scheme of my symbolism, the important takeaway is simply this: a public sector PR team is a lean, highly-specialized group of professionals that will provide support and guidance for your organization to maximize success in the government space. Full Stop.
Unique Needs of the Public Sector
Government agencies and the people that work within have uniquely different needs and offer challenges not seen in private sector businesses. They respond to their own language and terminologies – and traditional marketing buzzwords fall flat in the government sector. In order to engage and communicate effectively, your public sector PR program needs to speak to the distinct demands and needs of both the government official and their respective agencies’ core mission.
Simply inserting words like ‘federal’ and ‘government’ into your existing enterprise messaging is not going to cut it with government audiences. Government employees have their own language, with each agency having a distinct dialect with mandates, certification requirements, and other factors that dictate how they shape their needs as well as find vendors. Federal, state, local, and education entities each have needs and challenges you need to hand-tailor your approach, messaging, and engagement to truly resonate with these audiences.
By having a B2G Public Relations team, you gain the proficiency and experience required to establish your organization, brand, people, and offerings to the public sector customer in a manner that provides long-term stability and success.
State, Local, and Education (SLED) PR
Much like federally public sector PR – state, local, and education comms require a specialized approach and methodology in order to educate, help drive leads, and raise awareness for your brand and services – often in multiple target regions. This is where your public sector PR team will also show extreme value in that SLED communication programs can be executed from any location, giving your organization both awareness and presence in multiple target areas without the need to have permanent ‘boots on the ground.’
Why is this important now? Government contracting dollars and opportunities for state, local, and education (SLED) budgets have made a comeback in 2022, with states showing the largest annual spending increase in more than a decade and many reporting tremendous tax revenue growth from 2021. This, coupled with federal aid from the American Rescue Plan Act and the infrastructure bill, point to substantial opportunities with SLED entities – and the right PR and marketing strategy can help you take full advantage of these opportunities.

A public sector SLED team is specially equipped to handle multiple regions with different cultural, governmental, and social norms to help you project an expansive market footprint for your brand and expertise in mission-critical areas. Whether it’s in Houston, Texas, or Fairbanks, Alaska, a strategic SLED PR campaign will help establish your presence where you need it.
Public Sector PR Expertise
Public sector teams, their missions, and definitions of success come in all shapes and sizes, many times wholly different from the rest of the business – and your communications program and PR team need to as well.
I can’t tell you how many times I’ve heard, ‘I can just use my corporate communications team to handle public sector comms.’ The response to this is a simple question – ‘Are you using your corporate sales team to sell into the public sector?’ Of course not; you need your sales team to know your customer base and the specifics of the marketplace – so you have a team that specializes in the public sector customer. Your organization is making a strategic investment to go after government customers, and that investment should include communications that specializes (just as much as your sales team) in that customer space. While your in-house comms team or corporate agency might be able to help get you started, these efforts will only be table stakes if you don’t have a team that truly understands the federal, state, local, and education sectors.
There are countless unique differences between the public sector and business/consumer corporate communications. Understanding sales cycles, trends that will gain traction, how social media works in the government space, and how to most effectively engage the people who are going to help make a difference in your public sector strategy are just some of the key differences and capabilities a public sector PR team will bring to your team to help drive success.
Measuring Success for Public Sector PR
Historically, measuring PR success has always presented challenges, and traditional means of measurement are not conducive to adequately measuring or portraying success in the public sector. Most companies rely on measuring PR efforts directly back to sales, which in the public sector is a tough row to hoe. Our public sector teams are adept at benchmarking and measuring the metrics that count the most in the public sector.
They have the ability to measure web traffic, inbound leads from content and social media, the share of voice, and qualitative comments from customers and partners – data points your team can rely on to justify and optimize your public sector engagement and confidently measure your public sector PR success.
Find Your Public Sector PR Team
You are now asking yourself – where can I find highly specialized public sector communications professionals to support my needs? Regardless of the size of your company or government division, Bluetext can help you establish, engage and scale your communications to the public sector and get the most out of your communication efforts! Contact Bluetext to help your organization drive B2G brand awareness and lead generation through public relations.
The XXIV Olympic Winter Games have come and gone, in what felt like the blink of an eye. Even though the Games span only two weeks following the Opening Ceremony, there are years—and sometimes decades—put into their planning. A key piece of that planning is setting the visual identity of the Games, which is no small task. We all know the iconic five-ring emblem that symbolizes the union of international athletes, but each host city gets the opportunity to create its own unique logo. Olympic logos of the past have varied widely in color, type, and style, and each new logo is put to the test to tell a story not only about an Olympic season but about the host country itself.
A quick glance at all the different Olympic logos of the past makes it clear that there’s no clear-cut formula for an Olympic Games’ brand system (except the inclusion of the Olympic rings, according to the Olympic Charter). We’re going to take a look at the Olympic logos of yore and dissect our favorites and not-so-favorites through superlative-style judgment.
Best Abstract Use of the Olympic Rings — Atlanta 1996
Incorporating the Olympic rings is a requisite part of all Olympic logos, but that might get a little repetitive after over 50 Games. We appreciate the Atlanta 1996 logo’s integration of the rings with the column—the mark hints at the Olympics’ Grecian beginnings, the Olympic torch, and even manages to squeeze in the number ‘100,’ celebrating the centennial of the games.

Best Direct Use of the Olympic Rings — Innsbruck 1964
There’s something to be said for a simple, classic logomark like the Innsbruck 1964 logo. Using the coat of arms of the City of Innsbruck as a starting point, this logo features the rings prominently and uses an elegant typeface for the host city and year. We can’t think of a more classic, straightforward Olympic logo.
Best Out-of-the-Box Typeface — Rio de Janeiro 2016
The logo for the 2016 Rio de Janeiro Games feels like a celebration, exactly as its designers intended. This mark took inspiration from Carnival and uses organic forms and lettering to convey the energy of both Rio and the Olympic Games. This approach brilliantly tells a story while standing out from the crowd.

Best Out-of-the-Box Color — Sarajevo 1984
Working with the Olympic rings may feel constricting color-wise since there are already five colors to contend within a design. That didn’t stop the designers of the Sarajevo 1984 logo, who washed the whole logo in orange for the primary mark. This approach is particularly interesting because the logo was permitted to appear in any color so long as the entire mark appeared in a single color.
We’d be remiss to close this category without giving a nod to the London 2012 logo which, while controversial, was striking in its use of hot pink. They can’t all be winners, but we appreciate the bold approach.
Best Use of a Human Figure — Nagano 1998
In the Nagano 1998 logo, seven abstract human forms make up the petals of a flower, nicknamed the Snowflower. We like this mark not only because it defied expectations for a snowflake or other wintery symbol, but because it was the starting point of an environmentally-focused Olympic identity.
Best Minimal Logo — Tokyo 1964
Stunning in its simplicity and symbolism, the Tokyo 1964 logo is heralded as one of the all-time greats in Olympic logos. With the Olympic rings set in gold beneath a version of the Japanese national flag, this mark features traditional Japanese colors signifying peace and prosperity. Despite its minimalism, this logo manages to acknowledge the host country, the traditional Olympic identity, and the moral foundation of the Games.

Best Maximal Logo — Rome 1960
Poised between two relatively simple Olympic identities (Squaw Valley 1960 and Innsbruck 1964), this maximalist logo was an obvious pick in this category. In a departure from ‘60s graphic design trends, this mark harkens back to classical Roman motifs and styling. While it may not be everyone’s cup of tea, we admire the dedication to national legend.
Best in Show: Summer — Mexico 1968
Our winner for Summer Games logos has to be Mexico 1968. Not only does the logo incorporate the rings creatively, but it’s also reminiscent of athletic uniforms and traditional Huichol art. This mark is the basis of a fascinating brand identity—for starters, the official Olympic poster looks like album art. Sure, this logo may be a little busy, but what it lacks in refinement, it makes up for in energy.

Best in Show: Winter — Sapporo 1972
We love the Sapporo 1972 logo because it’s unlike any other Olympic identity, and it was perfect for its time. With a Bauhaus feel, this mark features the rising sun symbol from the Japanese flag, a stylized snowflake, the Olympic rings, and a single line of text. Despite including only basic elements, the unique stacking and coloring of these elements make this logo one of our favorites.
Best Iconography — Tokyo 2020
The iconography that’s developed alongside Olympic identities changes with the logo, and we wanted to honor an icon system that we think was particularly elegant. The icon set for the Tokyo 2020 games included icons (or pictograms) for each sport, including the five new sports introduced to the Olympics that year. Each icon is skillfully-made and coincides beautifully with the 2020 Olympic logo.
Judge’s Favorite — Munich 1972
A personal favorite that didn’t get identified in any of the above categories, the Munich 1972 logo’s name says it all—”Radiant Munich.” The abstract sunbeams are eye-catching, and the overall brand identity feels both joyful and serene.

Judge’s Least Favorite — Sochi 2014
While this logo was meant to convey sentiments of modernity and the coming digital age, it misses the mark. Suffice to say, there’s a reason that no Olympic logos in the 8 years since have included a URL.

There you have it—our take on some of the best and worst Olympic logos to date. We encourage you to explore all of these logos yourself on the Olympic website, and to explore other opinions like Milton Glaser’s for AIGA.
The logos for the Paris 2022, Milano Cortina 2024, and LA 2028 Games have all been unveiled, but given the controversy over and subsequent redesign of the Tokyo 2020 logo, we’ll wait to grade those logos until their respective Games pass. In the meantime, if you’re in search of a new logo or brand identity, get in touch with the team at Bluetext to learn how we can team up and go for the gold.