As the world has changed in the blink of an eye, so has the way we market to consumers. Now, more than ever, your website exists as BY FAR THE MOST IMPORTANT doorway to your brand and your brand experience. While stores stay shut, and face-to-face interaction is vastly limited, brands will rely on reaching their target audiences via their websites. Therefore, your website is mission-critical to your success.
Bluetext has published a 5 part blog series to help you think about and pressure test if your website is the best it can be.
Virtual Executive Briefing Centers are a valuable resource for companies wishing to show customers and prospects their full range of solutions in action, especially new solutions that the partner may not have implemented yet in its own organization. Customized presentations, live demos and in-depth discussions can be arranged. VEBCs offer a lot of great benefits for organizations including:
- Present your brand in a very innovative way with the latest HTML5 and video technologies
- Reach a wider audience, save money and drive efficiencies by reducing travel costs to visit a physical center
- Get your thought leaders delivering their message to a wider audience than their physical weekly calendar allows
- Deliver vertical specific messaging and solutions in a customized fashion
- Personalize the experience based on the understanding of the audiences job title, history with the enterprise, and other components the digital environment can capture and feed into the site
- Juice up your SEO with a smart build and customer journey that enhances your SEO footprint
Bluetext has had a lot of experience designing and developing Virtual Briefing Centers. Here are just a few examples of the innovation we have helped drive for our clients:
McAfee and Intel Security’s Future Agency
McAfee and Intel turned to Bluetext to design a campaign to demonstrate the advancements in cyber security that the companies are driving across the Federal Government. Named The Agency of the Future and found on the web at futureagency.com, the solution integrates an interactive, 3D experience and a series of videos with lead generation integrated throughout. The experience was enhanced with a continuous monitoring webcast that targeted federal IT security experts and drew more than 3000 leads. The campaign won major kudos at McAfee corporate.
CSC’s Digital Briefing Center
CSC’s Digital Briefing Center is where customers, partners and prospects from across the globe can come to learn more about the key technology conversations and market shifts CSC is driving into the market.
The center is driven with immersive 3D video technology that is completely interactive through Html 5 overlays throughout the user journey.
Following launch, Bluetext’s collaborative creation with CSC’s Digital Marketing team became the top performing component of the csc.com global web presence, a huge feat for a Fortune 500 corporation.
Version 2.0 features new capabilities spanning:

-
Multi-floor scalability
-
Triple screen experience
-
Dynamic social media integration
-
Triggered infographic visualizations synched with briefing videos
-
Chaptered video interactivity
The following video of CSC’s head of global brand and digital marketing talks about this project:
TalkShop by Cooper Thomas
From corporate meetings to conferences and workshops, connecting with your workforce and customers is an essential element of business. Bluetext was hired by Cooper Thomas to help enhance their virtual training and meeting services and next-generation virtual platform that can help their customers get the most out of their customers’ virtual events.
With their virtual event platform, you can now connect with employees, customers, and clients conveniently and cost-effectively. The unique speaker-training program guides your presenters to deliver more effective and engaging virtual presentations. The speaker coaches provide focused support to help busy subject matter experts become polished presenters. They also provide project management and program support for events ranging from single training sessions to multi-day conferences, as well as on-site support for virtual and face-to-face events.
As the world has changed in the blink of an eye, so has the way we market to consumers. Now, more than ever, your website exists as BY FAR THE MOST IMPORTANT doorway to your brand and your brand experience. While stores stay shut, and face-to-face interaction is vastly limited, brands will rely on reaching their target audiences via their websites. Therefore, your website is mission-critical to your success.
Bluetext has published a 5 part blog series to help you think about and pressure test if your website is the best it can be.
With 57% of the world’s population now on the internet, promoting your business through a website has become even more critical. Additionally, over 50% of website traffic comes from mobile, and over 66 million American adults now own a smart speaker with digital assistant capabilities. Your website is where a potential customer will get their first impression of your business, and navigating the way website browsing behavior continuously evolves can be tricky. Because having a poorly designed website can be worse for your business than having no website at all, turning toward an expert website design agency can help you find the best website solution for your company. An agency can help you stay on top of the latest web design trends, and bring both your website and your business to the next level.
User experience (UX) is one of the most important things to consider when redesigning your new website. According to Jakob’s law, users spend most of their time on websites other than yours. This means that users prefer for your site to function in a similar manner to other sites they frequently interact with. Staying up-to-date with current web design trends is imperative to keep your users engaged.
Bluetext suggests considering the following seven trends when building your website to ensure that your site combines SEO functionality with the best UX, boosting your brand’s presence online.
1. Make Mobile a Priority
Over 50% of all website traffic comes from mobile. With a user-base continuously becoming more dependent on mobile, it is even more important for website designers to prioritize and optimize web experience for mobile devices. Designers must create a thumb-friendly design to not only make mobile navigation easier for the user but also create a seamless, visually-appealing design.
More than 60% of companies reported an increase in sales after designing mobile responsive platforms; however, approximately 40% of people will leave your website if it isn’t mobile-friendly. While simply having a mobile presence may seem good enough, optimizing this experience through design to cater to mobile users is the most important factor.
If these statistics aren’t convincing enough, it’s also important to keep in mind that Google gives priority to mobile-friendly sites by ranking them higher in search results, positively impacting your SEO. Lacking a mobile-friendly experience can negatively impact your website’s ranking, whereas sites that are mobile responsive will often receive a ranking boost, even for searches on a desktop.
Check out some of Bluetext’s work on mobile with Paya and Mindtree.
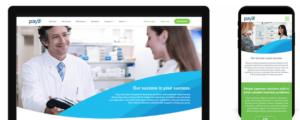

2. Increase Page Speed
It takes users only three seconds to decide whether or not they want to stay on your website. These three seconds are crucial to your website’s dwell time (aka the time a user spends on your website before returning to the search results). Web design agencies can provide creative solutions to help engage your users within these three seconds. Additionally, web agencies know the best tactics for improving page speed, such as image compression. Image formats like JPEG 2000, JPEG XR, and WebP often provide better compression than PNG or JPEG, which means faster downloads and less data consumption.
The less time it takes your website to load, the better your SEO. Because of the Google Speed Update, Google won’t prioritize your website to users if it will take too long to load. Taking your site to a web design agency will ensure that your website is optimized for the user, while also ensuring that you have the best possible SEO ranking.
3. Optimize for Voice Search
Page speed is also becoming more important as the number of smart speakers and digital assistants continues to grow. Over 66 million American adults now have a smart speaker, and designing a website that capitalizes on Voice Search Optimization is the only way to ensure that those using smart devices for their searches will have access to your site. Voice search is meant to be a faster, more convenient way to get information, and if your website takes too long to load, it is less likely to be returned for a voice search result.
According to a PWC study, 71% of respondents would rather use their voice assistant to search for something than manually typing their query into a search engine. The differences between these spoken and typed searches may lead to different SERP results, and if your website is not properly optimized for vocal search, you may lose ground to your competitors. Because vocal searches only result in one top result, everyone is vying for this “ground zero” position. You can obtain this coveted position by gaining Google’s featured snippet spot, which aims to directly answer users’ questions. Voice searchers are also more likely to search in long-form questions as opposed to using shorter keywords, so it’s important to consider the types of questions your target audience may ask, and to position your website well to answer these searches.

4. SEO vs. SEM: Choose Wisely
How can you tell whether to focus your marketing efforts on SEO or SEM? Let’s return to square one: what’s the difference? Search Engine Optimization (SEO) was traditionally thought of as a component of Search Engine Marketing (SEM), which comprised of both paid and organic tactics. However, this language is shifting, with SEM now referring exclusively to paid search. SEO is a method to optimize your website to receive organic traffic, while SEM is a way to funnel in relevant traffic from search engines by buying paid or sponsored ad listings.
So which is better to focus on for your website? SEO allows your business to get more visibility, building brand awareness at a low cost. Choosing keywords that are relevant to your website can earn you a spot on the first page of the SERPs, automatically earning you credibility and trust from search users. In order to increase your website’s chances of making this first page, follow these simple steps:
- Use relevant keywords in the URL to describe the content of the page
- Use your main keywords in the beginning of the title tag of your page
- Use the right keywords in the meta description of your page and make sure it is enticing enough for users to click-through to your site
- Use your primary keyword(s) in the H1 tag of your page
- Use your main keywords along with related long-tail keywords in the first few paragraphs of the page
SEO will bring your website brand visibility at a lower cost, but it’s important to invest in researching which keywords will best optimize your website.
While SEO is typically more sustainable, turning to SEM can also do wonders for your website. SEM allows you to capture the attention of your target audience by claiming a spot above-the-fold of the SERPs. Sponsored listings also give you more control over the results you achieve; every element of the ad can be customized and tweaked to target your audience. SEM charges on a per-click basis, and while this may be more expensive, it allows you to achieve quick, measurable results without going through the trial-and-error process that SEO typically involves.
Both SEO and SEM have their pros and cons, and both may be right for your business at different times. Turning to an agency that specializes in SEO and SEM will help you choose the right tactic at every turn.
5. Hello, Homogenous Hero
The fast pace of modern life means that people have less time to spend on your website. When they enter your site, simple and intuitive web design will allow them to quickly find what they’re looking for. The use of minimal design allows for the rapid digestion of information and ultimately leads to more satisfied users.
The inability to spend endless time searching for information on a website also means that many web design agencies are moving away from the once-popular ubiquitous site, and shifting instead toward the homogenous hero. Instead of boldly featuring the headline in the center of the landing page, designers are opting instead to move the header and CTA to one side, with the image on the opposing side. This split-screen aesthetic also allows for easy conversion to mobile, providing a clear dividing line between the two content blocks.
Check out some of Bluetext’s latest homogenous hero designs through their work with Centauri and Perspecta.

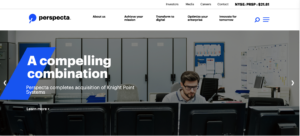
6. Animate Your Site
The use of animation is an easy way to make your website appear polished and dynamic. Animation also helps bring your brand’s story to life, quickly engaging users and drawing more visitors to your homepage. When used as a tool to communicate complex messages easily, animation can reduce the time that a user must spend in order to understand your message, which enables them to spend more time exploring your website.
When adding animation and motion into your website design, it is important to consider web image optimization, which is the process of providing the smallest-sized images optimized in terms of quality, resolution, and format. With the rise of internet browsing on mobile, images and animations must be optimized to perform well on mobile. While animations are a fantastic way to engage your site visitors, they can also slow down your website load times and negatively impact your SEO. Let a professional website design agency like Bluetext help ensure that your website can support lively animation without dragging down your website load time.
When Bluetext redesigned the Clarabridge website, we made sure to incorporate motion in a sophisticated way, making the UX come alive. We used motion throughout the homepage to engage the user and pull them further down the landing page. This design also quickly explains how Clarabridge works and allows a site visitor to visualize how they might best use Clarabridge’s services.


7. Incorporate More Video Content
Video content diversifies your web page, and also appeals to those fast-moving users who do not have the time to search through a lot of text. Videos are also a great way to make an emotional connection to your users and lead to a better overall website experience. By 2020, experts predict that 80% of online traffic will be video. Additionally, 72% of businesses say that video has improved their conversion rate, and 45% of people watch an hour or more of video per day.
While video content is clearly an important marketing tactic, 64% of marketers see video as the most difficult content to create. Not only do videos take time to plan, shoot, and edit, but it is also tough to decide exactly what type of content should be presented in your video. Because viewers’ attention starts to drop off after roughly two minutes, finding an expert who specializes in video content may be the best route for creating the perfect video for your website.
Not only will video content boost your website’s success, but it is also rewarded by Google. If your site includes video, it is 53X more likely to get a first-page spot in search results. Video improves SEO, which boosts your ranking. But if a short video is one of the first impressions a user will have of your business, how do you go about creating successful video content, and keep the user coming back for more? Many website design agencies have video specialists who can tell your story in a clear and powerful way. Check out Bluetext’s latest video work with Invictus.
Invictus Brand Essence Video, July 2019 from Bluetext on Vimeo.
“Should we be marketing right now?”
That’s the question a client asked for the first time the day before the COVID-19 pandemic was declared a national emergency by the federal government.
Since then, we’ve gotten the same question in some form by most clients and by every new business engagement at our agency.
In less than a week, we have reimagined a work environment that’s evolved over nearly two centuries, coffee spoon by coffee spoon, cubicle by cubicle, combo meal by combo meal.
Yet while it’s not business as usual, it’s still business and your customers still need your help.
Should we be marketing right now?
The answer is yes, and, if you think not, you may still be thinking about marketing all wrong.
Is Your Approach to Marketing Right?
In some instances, at the core of the question is an assumption that marketing is, by itself, invasive. And sometimes that’s true. Poorly planned buys that target the wrong audience, campaigns that haven’t been well-conceived that add noise to noise, awareness campaigns that do nothing but thump your customer against their forehead.
Remember first and foremost that marketing isn’t really about you. It’s about your customers.
It’s about what you can enable them to do. Your marketing should never be an unwelcome intrusion to talk about your company. It should always focus on customer enablement. If it’s an awareness campaign it should be authentic and meaningful, not merely an expensive version of a pop-up ad.
Of course, we may not recommend launching a new campaign in the teeth of a news cycle dominated by a global crisis. You can check Ad Age’s list of brands’ marketing response to see a few of the major brands who have delayed new campaigns. But even among the largest brands, the trend hasn’t been silence, but adaptation.
Why Continue Marketing?
Your Customers Need your Help. As much as we may like to think the reason to run a business is to create great marketing campaigns with an agency like Bluetext, ultimately businesses exist because you have a service you think can help other companies or individuals. And you’re right. Marketing may interest or make potential customers aware of a product, but the reason they buy isn’t the company, but the solution it offers. While customer needs may have changed, the fact that needs exist hasn’t changed.
It’s Now your Primary Contact Vehicle. Business-to-business and business-to-government sales are a high-touch sales market now in a no-touch world. Your digital marketing is now even important to maintain relationships. Webinars, email campaigns, video, and virtual events are now a critical way to maintain relationships when the days of hosted lunches and in-person meetings are temporarily in the past.
Even consumer brands like restaurants or sports lose their primary touch-point in the in-person experience. But that doesn’t mean they should surrender their place in the consumer’s mind.
Your Brand Journalists Know the Answers. The specialization of products and services has expanded massively at the same time traditional media has declined. Brand journalists have filled the gaps to be experts on their company’s offerings and their industries. Questions about VPN services or season ticket plans aren’t going to be answered by the media. Understanding how you can modify SD-WAN to best handle the surge in traffic for the shift to BOPIS at a retail level and telework on a corporate level won’t have its own segment on CNN. The answers aren’t coming from traditional media gatekeepers. They will come from your marketing teams. Brand journalists can provide expertise about the market.
Because Information Is Always Better Than Silence. Reacting to a story puts a brand in a weaker position than telling its own story and moving the narrative forward. Saying nothing puts a brand in a worse position. Customers and prospects want to see that you have an understanding of the situation and that you’ll be able to continue to provide service. Companies will be able to build goodwill for their brands by instilling confidence in their customers.
What Should You Do Differently?
While you should continue marketing during the COVID-19 crisis, that doesn’t mean you should act as though nothing has changed.
Think about your tone. Realize that no matter how big or small a company may be, they’re all made up of people, people who deal with the same challenges and same stresses the rest of us are dealing with. Kids have to be monitored, communication tasks are more complex than ever (be prepared to hear “I’m sorry, I didn’t realize I was on mute,” between six and six thousand times a day).
Change the way you speak just as you would in real life. Make sure your messaging guides include standards on tone and conversation and aren’t just the partial script of tag lines and message maps. We were already beyond a world of one-way communication in marketing and now it’s even more so.
Be sure your brand is empathetic and helpful above all else.
Rethink Customer Needs and Challenges. Pull your campaign strategy and brand guides off the shelf. Review the customer wants, needs and challenges. How have they changed? How has your ability to deliver them changed? How does it impact your overall approach? The key to great marketing is understanding your capabilities and your customer wants and finding the point of intersection.
Polish Your Digital Presence. Your website, your apps, your social, your display ads. Your digital marketing is now your front door. (Of course, we would argue this was true long ago.)
- Be sure your website is prominently conveying information most useful to your customers in light of the COVID-19 crisis.
- Be sure your website is communicating everything your customer needs to find, interact and communicate with you.
- Spend time thinking about SEO. Examine your meta summaries and the language that appears on results pages. Think about how search behaviors are changing.
- Take a closer look at your social properties. Are they relevant to your customers and employees? As the remote workforce finds new ways to foster two-way conversations, your social sites represent an increasingly important space to communicate internally and externally.
Be Smart About Tactics. If you have the budget to do it, display ads may never be more useful. With the world behind computer screens, there has never been a better chance to reach a larger audience, segmented by any number of demographic factors to reach the people you can help. Even social media sites like Twitter and Facebook, long a small impact for business-to-business at best, are a potential opportunity. In 2019, Pew Research estimates 62% of people got their news from social media. The drive for more news, faster, is likely growing the presence of your customers on those platforms.
If marketing budgets are already a challenge, get creative. Focus on earned media. Spend time working on your SEO. Think about the best ways you can demonstrate a commitment to your current customers in ways that are not just noise, but meaningful to them.
Take a Deep Breath. The situation we find ourselves in likely isn’t going to resolve anytime soon. And as the adage goes, while few people remember if you do it fast, everyone remembers if you do it right. Having the first word is never as important as having the right word.
Keep Connection Going. The COVID-19 crisis will shuffle the deck for businesses. It’s time to rethink customer needs and usage patterns across all industries. It’s time to think about the acceleration of business trends like the remote workforce of curbside pick-up for brick and mortar stores.
But it’s not time to stop helping customers. It’s not time to stop telling your story. It’s not time to stop marketing.
Additional Resources:
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) | CDC.org
- COVID-19 (Coronavirus) Pandemic | 211.org
- Coronavirus (COVID-19): Small Business Guidance & Loan Resources | SBA.org
- Guidance on Preparing Workplaces for COVID-19 | OSHA.gov
- Government Response to Coronavirus, COVID-19 | usa.gov
- Virus Outbreak: The Latest News | Associated Press
This Sunday, the Kansas City Chiefs will square off against the San Francisco 49ers in Super Bowl LIV; anticipated to be one of the most entertaining sporting events of the year brought to you by gunslinging quarterbacks Patrick Mahomes and Jimmy Garoppolo.
Thanks to two electrifying football teams and the unofficial holiday that comes with Super Bowl Sunday, a projected 100+ million viewers in the U.S. will tune into FOX at the same time, creating an unparalleled opportunity for marketing pros to cultivate a memorable brand association with more than a quarter of the U.S. population.
But these opportunities do not come cheap
Outside of the cost of producing the commercials, (which anyone in marketing can tell you isn’t cheap) you have to pay egregious dollar figures just to place it on the primetime Super Bowl stage. FOX sold out of its Super Bowl ad slots in late November, which reportedly sold for between $5 million and $5.6 million.
$5.6 million!
Let that number sink in. $5.6 million could buy you a five-bedroom house with a view of the Golden Gate Bridge in downtown San Francisco. Or 10 five-bedroom houses in the Kansas City-area. Suffice to say, there’s a lot you could do with that money.
From a marketing standpoint, if your brand is considering purchasing a primetime 30-second Super Bowl ad, or you’re simply wondering how you could make a splash during the event without blowing your entire annual budget, consider these marketing alternatives that you could buy for the same price:
1. 20 years of a PR retainer at 20K per month
While it probably does not make sense to stretch one year’s marketing budget over the next two decades, this illustrates how far your marketing dollar could go over time with a PR budget as opposed to a single, 30-second Super Bowl ad. A monthly PR retainer could produce the ability for your brand to demonstrate expertise to more targeted audiences than the general public watching the Super Bowl at a fraction of the cost. This is typically executed with media relations and strategic placements of messaging within publications of interest to the brand’s most important audiences. Spending your marketing dollars in this way would create a steady burn of messaging over a long period of time as opposed to one, 30-second firework explosion of your brand that a large portion of the Super Bowl audience could miss.
2. Multiple omnichannel digital campaigns
In order for any Super Bowl campaign to be successful, it must eventually migrate to the digital realm in one way or another. Outside of the $5.6 million it will cost to run the ad in the spotlight, brands also have to shell out at least another $1 million to market the ad via social media. So why not go straight to digital with your campaign?
Newcastle Brown Ale was among the first to attempt this digital-first Super Bowl strategy in 2014 with a satirical YouTube commercial featuring Anna Kendrick about the Super Bowl commercial they almost made but didn’t have the money. By posting the video directly to YouTube and spending all of their resources marketing the commercial online, they found a witty way to poke fun at the nature of Super Bowl commercials by making one while also saving A LOT of money in the process. Digital campaigns can be an extremely effective (not to mention more targeted) way of maximizing your exposure to your key audiences. Ultimately the third-party validation that will come from individuals sharing your content will be the mark of a successful campaign, so digital-first strategies could be the next iteration of Super Bowl commercials.
3. Yearly platinum sponsorships in ten of your audience’s favorite publications
If your brand is targeting audiences that congregate around specific media outlets, paid partnerships with those media outlets can be a great way to enhance your exposure to the people who matter most. Sponsorship packages at media publications vary based on their target audience, the type of content they typically publish, and what you’ll get for your spend. But with big dollar figures in the hundreds of thousands, you could expect millions of unique viewers, digital ad space, thought leadership content, lead-gen, sponsored webinars, and more!
As Americans and football fans around the world tune in to the game on February 2, household brands will be vying for your loyalty and lesser-known companies will be introducing themselves to the world on the hottest advertising real estate money can buy. However, you can also expect to see many organizations turning to alternative marketing to make their splash during the game.
The real winners of this international media event will not be limited to just the Chiefs or the 49ers, but also to the organizations who strategically employ ALL of the marketing tactics available to them.
Progressive marketing organizations are continually evaluating their approach to their brand & logo to ensure they are viewed as forward-looking and ahead of their markets. Halfway into 2019, there are a number of trends that have been making headway when it comes to this important creative and design work. Courtesy of the folks at Logo Lounge, a repository for designers to post and share their work, we have a sense of what changes are making their way into the market. As Logo Lounge is quick to remind us, when a client makes its logo selection from a typical range of five options, that also means that it has rejected the other four.
Here are four trends getting attention by logo and brand designers:
- Adding motion through “spot drag.” Spot dragging uses circular dots with tails to add a touch of motion to a logo. They give the impression of immediacy as if this logo just happened, and the ink is still drying.

- The Period makes a stand. A refinement of the recent punctuation trend, using the period in a logo gives it a little more power. Especially when it’s is used to signify something altogether different (like completing a different letter), a period makes room and draws the eyes in.
![]()
- Quarters make a play. One trend that can be seen everywhere is the use of “quarters” in logos – not the coin, but the geometric shape, which is simple and distinctive. It has balance and is being used with vibrant, solid colors. Sometimes used alone, other times with other geometric shapes, these add a purity of form that underlines the value of the brand.

- More layers. While simplicity works with many established brands, adding more layers and details is making a push into 2019 logo trends. The advantage of this approach is to invite viewers to look more closely and engage with the logo to understand what it’s trying to convey. Just don’t go overboard – two layers works, more than that can just look messy.

Learn how Bluetext can help you design a new brand & logo for a greater impact in the market.
It’s pretty obvious that videos placed on YouTube have huge appeal with consumers who love to be entertained while seeing a product or brand in action. YouTube videos can be cutting and funny, irreverent or just dumb, yet they have the capability of capturing consumer attention and driving interest and conversion. Good videos translate to more sales—according to one recent survey, consumers are nearly two-thirds more likely to purchase a product after watching a video.
But how well does that work for enterprise and business-to-business companies? Do videos on YouTube help with marketing when the the target buyer may be a busy executive, the sales cycle can be long, and a variety of different types of individuals may have input into the decision?
With B2B and enterprise products and services, it is even more important to leverage a channel as important as YouTube. Here are a few simple reasons why:
• YouTube is the second most frequently used search engine, which not only means that your target audience is probably researching solutions on YouTube, but also that a properly labelled and tagged video can show up high in the search results;
• Attentions spans are getting shorter, and a tight video or animation can capture that attention better than words or images on a web page;
• It offers strong opportunities to engage with your target customer; and
• It allows you to show off your creativity and position your company as a thought leader in your market.
Here, then, are six tips for how to leverage YouTube for B2B marketing:
1) Short is Sweet. As recently as two years ago we were producing videos up to five minutes in length to showcase brands and their executives. That time has dropped by more than half. A recent study confirmed that the most successful videos on YouTube are under two minutes in length—and those around the one-minute mark are the most popular.
2) Set Up a Branded YouTube Channel. Creating a company channel delivers a better experience than individual uploads, even if the titling and tags are already aligned for the best search results. A branded channel allows for a branded experience, with creative elements that showcase the company or product. It also allows a company to segment the videos so that the target viewer can better find what they are after.
3) Be Disciplined About New Content. Just like your other social media platforms, YouTube thrives on consistent content. Just posting video without a regular refresh leaves too much silence and no reason for a viewer to come back. When you develop your YouTube strategy, make sure you can add new content on a regular basis for a sustained campaign.
4) Treat Your Video Like a Blog Post. Don’t waste the opportunities to drive traffic to your YouTube channel through other social media platforms. Think of it as you would a blog post. The more nurturing it gets from all of your social activities, the more traffic it will get. So tweet it, blog about it, post it on Facebook, and promote it through your email newsletters.
5) Advertise. Remember, YouTube is owned by Google, so you can promote your videos through Adwords for Video. There are currently three ways to advertise and drive traffic to your channel: as a pre-roll ad before the videos that viewers watch; as a banner ad when people are browsing and searching the Internet; or as a promoted video when people are searching for similar videos. Each requires a careful selection of keywords to make sure you are getting to the right targets.
6) Be Creative. A static video of an executive talking about the company won’t capture anyone’s attention. If it’s meant to be instructive, consider using animation to tell the story. If it’s a thought leadership campaign, then have experts discussing trends. Use multi-camera shots, tight editing, and professional sound and lighting to keep it engaging. It’s ok to be entertaining, but it also needs to give viewers the information they are searching for.
YouTube should be a key element in every campaign’s mix of platforms to reach and engage the right audiences. It provides the audience with visual content that can showcase the brand, and it’s easy to gather the analytics about what is working and what’s falling flat. It requires a disciplined and smart approach, but the results of a smart YouTube campaign are more engagement and conversions.
There are many aspects to consider in web design, and one important feature to ponder is the user journey. There are many means to target an anonymous user, identify who they are and their needs, and direct them to the relevant content on the site. Here are a few reasons why you should allow users to select their own user journey on your new website.
Direct Traffic. By identifying the user early in their interaction with your website, the more effectively you can direct users to content they would be interested in. From a UX perspective, the user’s experience on the site is swift and efficient. From a business perspective, anonymous users are quickly identified and funneled to custom tailored content. A notable example of directing a user’s journey is Bluetext’s recent launch of CQ Roll Call’s newly branded website: https://info.cq.com/
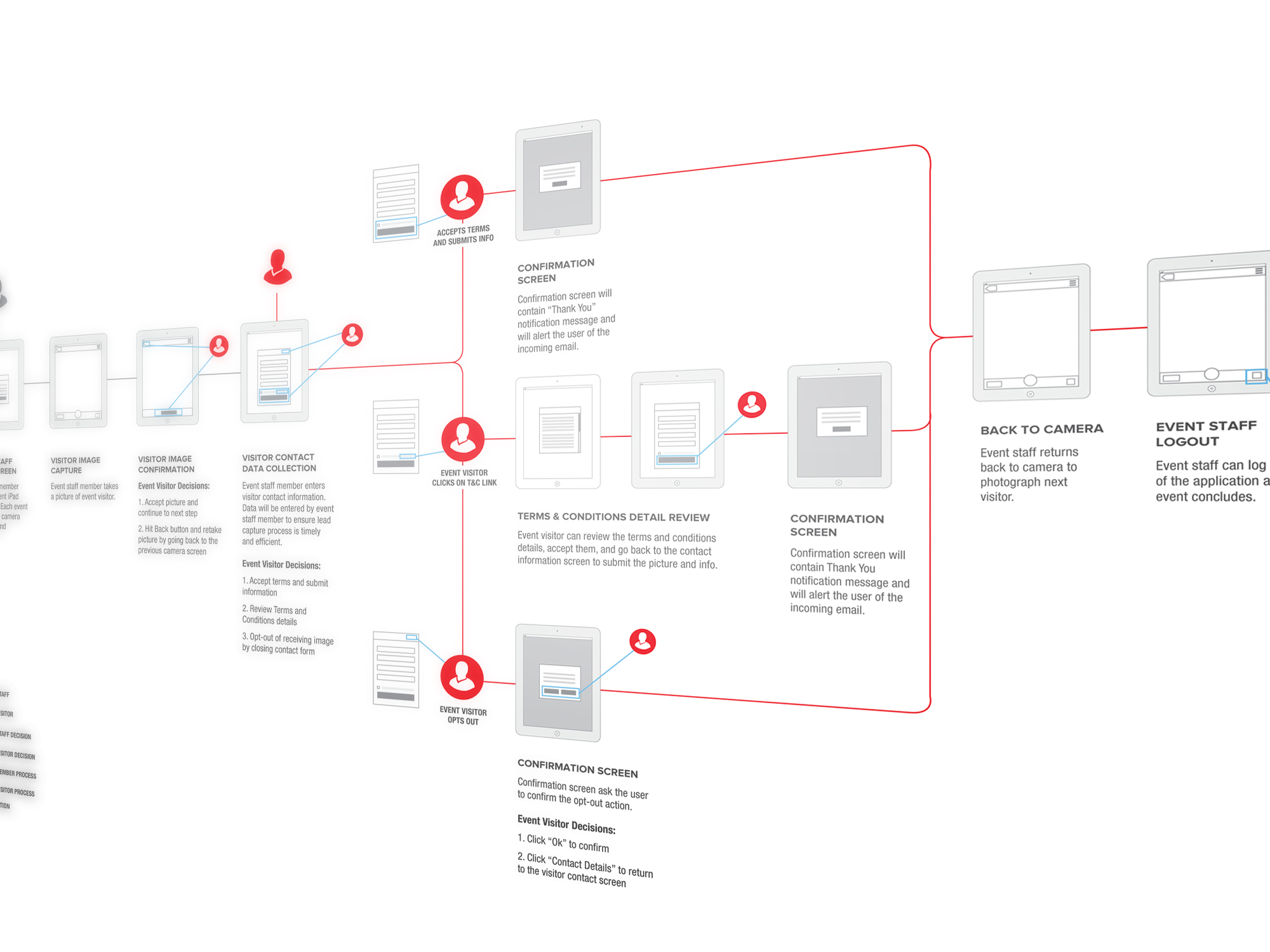
User Personas. By choosing to define user personas on its website, a company is able to identify functionality needs on other areas of the site at a high level. Personas define every aspect of each consumer group, and by mapping out a user’s journey a company is able to understand the key tasks each persona would expect to perform on its website.
User workflow. When a company is able to understand the flow of how different users would interact with its website, it is able to use this information to ultimately inform its website interface and provide its users with the best possible experience. Web design agencies are experts in this area to implement the optimal interface specific for a company’s users.
Identifying a persona and their user journey through a website increases efficiency on both sides. Users want to view what is relevant to them and companies want to be able to tailor content to target consumer groups. Defining a company’s personas ultimately informs the user experience design for an overall superior experience.
Looking for best in class digital marketing? Contact us.
Speed is by far the most critical metric to consider when re-designing an enterprise website – it won’t matter how beautiful your new site looks if nobody is going wait an extra millisecond for your homepage to load. In addition to providing a fast loading, responsive user experience – speed has a direct impact on your ability to optimize higher user engagement, conversion rates and SEO rankings – all of which drive better brand and marketing performance.
One of the primary signals Google’s algorithm uses to rank performance is site speed – but by extension it is really page speed that Google is measuring. According to Moz, page speed can be described as either “page load time” (the time it takes to fully display the content on a specific page) or “time to first byte” (how long it takes for your browser to receive the first byte of information from the web server).
Page speed is also vitally important to user experience – pages with longer load times tend to have higher bounce rates and lower average time on page that result in an immediate negative impact on conversions. According to Google, 53% of users will abandon a site or web page if it doesn’t load within 3 seconds. This also has a direct impact on search rankings – with less than half a second separating the first and third pages of Google search results.
So how do you measure site speed? Google introduced its own web-based tool, accessible via Google Labs, called Page Speed Online. It’s available as a web-based tool as well as a Chrome extension. With it, you can quickly get an overview of high priority, medium and low priority fixes that can help increase your page speed.
Here are the top 5 for your digital agency implement to add instant horsepower right out of the gate:
- Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) Technology – AMP is a new open framework built entirely out of existing web technologies to dramatically improve the performance of the mobile web by enabling code to work across multiple platforms and devices so that content can load instantaneously —no matter what type of phone, tablet or mobile device you’re using. With Google splitting its index into separate versions for mobile and desktop – the time has finally come to start prioritizing mobile
- Wrangle Your Javascript and Stylesheets – Have your scripts and CSS load in external files instead of cramping up each and every web page. This way, only the browser has to load the files one time, rather than every time someone visits each page of your site. Ideally, put your external CSS in the portion of your site, and your external Javascript file as close to the tag as possible. As a result, the browser isn’t bogged down wading through all those requests for external files right from the start. The only time you won’t want to do this is if the Javascript needs to load near the top of the page – such as to display a name or load up an image carousel.
- Optimize Your Images – In Photoshop or Fireworks, you can use the “Save for Web” option to drastically reduce image size. An image quality slider lets you see the visual trade-offs between graphic file size and crispness. Also – don’t rely on HTML to resize Images – while HTML makes it easy to create a smaller version of a larger graphic it doesn’t mean it’s taking up any less room on the server. The browser still has to go through the process of loading the entire image, checking the width and height you want and then resizing it accordingly.
- Use GZIP compression – You’ll want to ask your web host if they use GZIP compression and deflation on their servers. These are two techniques that can significantly speed up a site, reducing file size by as much as 70% without degrading the quality of the images, video or the site itself.
- Caching – Many content management systems now have plugins that will cache the latest version of your pages and display it to your users so that the browser isn’t forced to go back and dynamically generate that page every single time. Plugins like WP Super Cache can take a serious bite out of page load times.
You can also look beyond your website itself and consider a Content Delivery Network (CDN) that serves up pages depending on where the user is located. Faster access to a server near their geographical area translates into faster load times.
While speed is the most critical metric of any re-design effort – it’s not the only metric. Working with a smart digital agency to define KPIs for the re-design of your next generation website will significantly improve performance metrics across your digital marketing ecosystem right out of the gate.
Go the need for speed? Contact us
Top digital marketing agencies are quickly learning that mobile retargeting is now a key element in any successful campaign. But moving our clients to this strategy is not always an easy sell, as the many challenges that mobile presents can be intimidating. In spite of the roadblocks, mobile retargeting can increase reach and engagement far beyond other channels. Here are Bluetext’s six top tips for getting started with a mobile strategy:
- Unsure on how to reach target audiences on their mobile devices? Think social media platforms. Today’s target audiences are more likely to browse their social media apps on their mobile than search websites. Take advantage of the tools that Facebook, LinkedIn and Twitter offer for their ad campaigns.
- Want to increase mobile traffic to your site? Optimize your website for mobile to fully take advantage of this platform. That means a design that is responsive for all devices, and features simple and concise headlines, titles and other text. More importantly, make sure that images are sufficiently compressed, reduce the number of redirects (nobody wants to wait for a new screen to load), and minimize code to maintain a high-performing experience.
- Not sure how to design for mobile? Think like a visitor to your brand would, accessing your site via a mobile device. That means simplified designs and copy, but also calls-to-action that are clear about where the visitor will land if they click on that button. Viewers don’t want to leave the screen they are on unless they know there they are going.
- Need to improve your reach on mobile? Safari is the leading browser for mobile devices, but leveraging Apple’s tool is not so easy. One simple trick: Make sure you are enabling Safari, which typically blocks third-party cookies in its default setting. Find a provider that is skilled at accessing Safari’s massive number of users.
- Still not seeing the conversions you expect? It could be your landing page. Try to simplify the actions on the landing page to make sure there is no confusion or abandonment from that conversion point.
- Want to get hyper-specific with your targeting? Try geo-fencing for conferences, events, shows and other gatherings of target audiences. Sophisticated new geo-locating tools allow geo-fencing to specific blocks around convention centers, hotels and other venues. Serving ads at the right time and place can pay big rewards.
Any marketing campaign can be much more effective with a mobile component, as long as it’s well-executed.
If you want to learn more or need help with your campaigns, Bluetext can help.
It’s almost January again, already! With 2017 almost behind us, amidst the holiday cheer and eggnog, it’s also time to reflect on 2017. It goes without saying that today, changes in digital marketing happen within the blink of an eye. There’s simply no better strategy for your business than a continual adaptation; the years of resting your laurels with time-tested methods are long gone. What works best with digital simply changes too fast, and nothing is really stable.
With that in mind, we know how busy you are this time of year, so we’ve gotten together and brainstormed what we believed to be a list of the most important digital marketing trends for 2018. It’s a big list, but we’ve narrowed it down to just a top four. We invite you to take a look — if only to just keep up with the ever changing modern media environment.