A lot happens every 60 seconds online across digital platforms. In fact, a staggering amount of posts, uploads and emails take place in the space of a minute – every minute of every day. By looking at this data in detail, and comparing trends over the past three years, marketers can glean a lot of useful insight as to where to focus their brand’s attention when developing media programs – whether for specific targeted campaigns or for ongoing outreach.
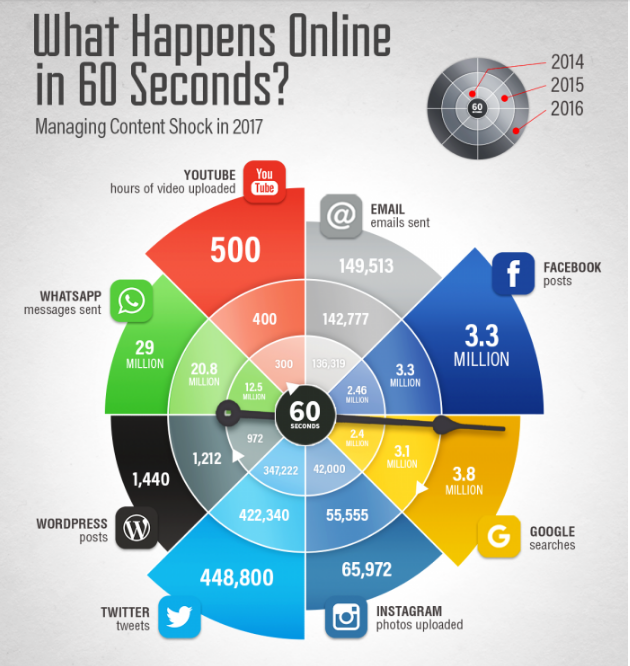
A collection of these stats across the most important platforms was recently published by SmartInsights, and it reveals some significant trends. First and foremost, the 800 pound gorilla platform in terms of activity isn’t Twitter and it isn’t email. It’s Facebook. While there are nearly 450,000 Tweets every minute, there are 3.3 million Facebook posts in that same amount of time. In fact, if you said that Facebook literally dwarfs the other contenders, that would be accurate.
 Except when it isn’t.
Except when it isn’t.
As the stats show, the outlier that is the largest by far is What’sApp, the free cross-platform app that can do just about what every other app does, and encrypt it in the process – with more than 29 million messages sent every minute. It’s widely popular around the globe (although not so much in the United States yet).
And who owns What’sApp? Facebook, of course. See a trend here?
60 Seconds Online: Where to Focus?
So where to focus your media campaigns? Look at some of the trends for what’s growing the fastest, and what’s being left behind. For example, Twitter’s 2014-2015 growth line came way down for 2016. Yes, there are more Tweets than a year ago, but not by much. Facebook shows no growth from 2015 to 2016 – which could mean that it has reached its upward potential. On the other side of the spectrum, YouTube and Instagram have increased their activity significantly.
Let’s not forget – Facebook also owns Instagram, while Google owns YouTube. So the upstarts are really just growth opportunities for the giants who continue to battle it out for dominance.
What does all of this mean for marketers? We tell our clients to look at where the growth is, not what was hot two years ago. Twitter is great for sports, entertainment and politics, but not so strong for b2b marketing. Instagram, on other hand, is expanding its reach across demographics, and can reach new target audiences that may have not been a focus of previous campaigns.
Thinking about your marketing and media mix? Contact Bluetext
Having worked with Drupal 8 in a production setting at one of the top development agencies for the last 15 months, I feel that I can responsibly say that Drupal 8 is ready for prime time. In fact, given all of the great improvements that the platform has to offer, it’s hard to think of an scenario where I would recommend Drupal 7 to a client. These include a standardized Symfony2 framework, a twig templating system, partial page caching, configuration management, layouts, and much more.
To learn more about Drupal 8’s new features, I spent a day recently at DrupalCon Baltimore, an experience that has heightened my excitement about Drupal and the future of the platform. Here are the takeaways that we got from the conference:
- Focus on Lowering the Barriers of Entry
- Core initiatives targeted at improving content authoring
- Revamped Release Cycles
- Drupal maturing in large enterprise
Opening the Flood Gates
The Driesnote was amazing as always. This one was more exciting than usual as there was a strong emphasis on the community and the shift for Drupal to become more user-friendly and lowering the barriers of entry. From a technical standpoint, the standardization on the Symfony2 framework and the addition of the twig templating system make working with Drupal more attractive to PHP developers, opening the platform up to a much wider developer market. From the content side, Dries highlighted the work being lead by Keith Jay to provide a better out-of-the-box experience to all users.
Content is King
In an ever changing market, it is important to stay ahead of the curve and adapt your organization to meet the needs of your client base. We validated a big shift that we are seeing in the market where the decision-maker is no longer the IT team – It has shifted to the marketing team. It is great to see Drupal follow this trend with the strong focus on the new core initiatives around UX, such as layouts and in-place editing. Dries also highlighted Cristina Chumillas for her work in improving the UX of several core pages.
Maintenance made easy
Another exciting announcement was around the revamp of the Drupal release cycles to make core upgrades for both minor and major versions of Drupal easier. The new 6-month cycles have been running great, and I for one am excited to see it. In this new model, functionality will slowly be deprecated (instead of removed) throughout the minor release versions as new functionality is added. This will give module developers an extended period of time to upgrade. Major releases will go one step further and remove the set of deprecated functionality to start the codebase off on a clean slate.
Climbing the Corporate Ladder
Drupal continues to gain traction in the large enterprise space with organizations and marketing teams looking to spend more of their budgets on content and campaigns rather than recurring subscription fees. This can be validated by the uptick in features and functionality that the community is providing for Drupal 8. As the market changes, so should the technology. The greatest thing about Drupal and the community around it is that we are the ones choosing the direction of the platform. We have thousands, or even hundreds of thousands of people validating this platform in the market and pushing the direction of the platform forward.
Bluetext continues to grow its commitment to Drupal and the Drupal community. If you are considering Drupal for your digital platform, please contact us. We would be happy to help you think through your approach to ingesting this powerful platform to power your growing digital ecosystems.
So, you want to sell to the federal government?
Good. Every year, Uncle Sam and his army of acquisition specialists have money to spend to achieve the critical missions of the federal government. In 2014, the most recent data available, the federal government spent nearly half a trillion dollars on contractors.
But there’s still another question left.
Who are you selling to? And I don’t mean which agency or which department. I mean, who?
Every contract issued by the government has a signature on it, an actual person who has selected your company to provide a product or service. Behind the signature are a small group of influencers. So, of that half-trillion dollar enterprise, your opportunity probably has been shaped by fewer people than are on an NFL roster.
So we ask again, who are you marketing to? Are you marketing to The Government or are you marketing to those who matter?
Why Personas Matter
Federal contracting is its own subspecies of marketing. We don’t have the intense feedback cycles or as many point-of-sale validations.
At Bluetext, we’ve helped dozens of clients reach the right government customers with carefully designed strategy backed by creative that makes an impact. It’s not always the same as business-to-business marketing or business-to-consumer, but one area that never changes is persona creation.
Why?
The government is not a single entity. It comprises agencies and departments, which in turn comprise directorates and activities and program management offices and thousands of personnel who play a role in acquiring products and services on behalf of the government.
How you reach them all won’t be the same. The avenues available to market to a program manager in the access-controlled world of the Intelligence Community, for example, won’t be the same as those available to reaching a director at the National Institutes of Health. Their missions aren’t the same, their needs aren’t the same, and their pain points aren’t the same.
Even within your target opportunity, your approach must vary.
Unlike traditional commercial services marketing, where you may aim for a thousand buyers of a million dollar contract, in federal marketing you’re more frequently aiming for one sale of one 100 million contract influenced by a dozen people. Not only does the persona exercise of understanding who your buyer is matter in fed tech, it matters even more.
Government Personas, in Four Broad Strokes
Directors and Deputy Directors and High Ranking Government Executives
This is typically the big ideas crowd. They’re usually looking for what’s next. Their interest is less day-to-day and more focused on how to better achieve their agency’s mission. Major changes begin at this level, whether it’s a product like a weapon systems or the federal cloud-first mandate, which has reshaped federal IT since its issuance by the then Chief Technology Officer of the United States. In the Intelligence Community, the largest IT transformation in its history began as a plan issued from the Director of National Intelligence.
Be bold and be visionary. If you want to radically change the government’s mindset, this is where you enter the bloodstream. Personnel in these positions aren’t always technically savvy and often have a more generalist approach to their departments, but they’re always eager to find the next great idea. They’re intensely focused on mission achievement, so help them understand how your solutions helps them better achieve the department’s goals.
Contracting Officers & Program Managers
What is a contract for your company is a career decision for contracting officers (COs) and program managers. On most acquisitions, the PM and the CO (or KO, as it’s often abbreviated, particularly in defense) are the most important decision maker. The program manager will be responsible for oversight of all the requirements in the proposal and of its execution once underway. The CO/KO can later modify the contract to add scope.
While PMs and COs appreciate the big idea, they are also intensely interested in the nuts and bolts and your capability to deliver. Every contract is an act of trust between these two positions and your company. These are experienced government personnel with whom you’ll want to build a long-term brand relationship. Depending on the size of the contract, they may not be subject matter experts in all technologies involved, but will likely understand enough to separate contractor-speak from actual capability.
Acquisition Influencers
For competitive bids, acquisition is done through an evaluation board which helps advise the source selection authority on its choice. Acquisition influencers are often subject matter experts and will be interested in the details. While their interest is in the proposal before them, your marketing should include this group as well. Are there third-party validations you can include to bolster your technical credibility, such as CMMI appraisal or AWS or Microsoft organizational certifications? Is your accounting system approved by a government auditor? Can you demonstrate applied expertise in your area of work, through white papers and blog posts? The big idea is great, but this is the group that will pop your marketing balloon if your big idea is all hype and no substance.
End Users
The role of a federal contractor is never simply IT for IT’s sake or product for product’s sake. It’s about empowering the end-user to achieve agency mission. And while the end-user, be it a help desk technician, a service member or a scientist, won’t sign a contract, their opinion of your product or service, particularly once it’s in use, will heavily influence whether it continues to be in use. Prior to acquisition, a groundswell of support could be cause for a pilot program. Market to the end-user’s pain points, rather than a technology-first view.
Every contract is different and Bluetext has helped dozens of clients craft specific marketing strategies by agency and by opportunity.
But like all marketing, it doesn’t just start with the what, it starts with the who!
Digital marketers are struggling mightily to understand how to reach consumers and prospects across social media. A platform that looks like the dominant king one day may quickly slip behind in new adoption and usage. Today’s trends may appear to be little more than a flash in the pan tomorrow. The challenge for marketers is to understand which platforms to leverage and when to reach new audiences, especially those key younger age groups that actually are the trend setters, even when those audiences have proven to be impressively fickle.
New research of Generation Z shows just how tough it has become to discern long-term trends with social media, and confirms how fleeting its members’ infatuation with previous leading platforms really is. The survey, of more than 300 college and high school students, the core demographic of Generation Z, was conducted earlier this month by the market research firm SCG. The top findings – not too surprising: This age group loves social media, and visits its favorite platform upwards of 11 times each day. What is surprising: That platform isn’t Facebook or Twitter. In fact, these younger millennials are all about Snapchat.
According to the survey 78 percent said they were daily Snapchat users, while slightly fewer–76 percent–reported using Instagram every day. Facebook was down to 66 percent. And while that not might not seem like a huge difference, consider that Facebook is now the granddaddy of social media yet a full third of the next generation of users are not tethered to it. They really like SnapChat’s fun new features, such as the different augmented reality lenses that were such a hit last year and its Geo-fencing tool. And before feeling sorry for Facebook, its dominant position in the market, including not just Facebook but its ownership of Instagram and WhatsApp, means it will be the 800-pound gorilla in the market for years to come.
Looking for an effective approach for your social media strategy?
Give us a call and see how we can help.
Well…given the polarizing nature of the 2016 presidential election, it’s a fair bet that families will spend as much time on Thanksgiving “talking turkey” as they will devouring it. The phrase “talking turkey” has an interesting history, with some tracing it back to colonial times to describe when colonists and Indians would barter over wild turkeys.
Since then, the phrase has been primarily associated with stating something frankly and matter-of-factly. I’m sure there will be plenty of frank comments at the Thanksgiving dinner table about how a Donald Trump presidency will impact the stock market. The energy sector. Foreign relations. The economy. How about the cupcake industry? Ok, so Red Velvet cupcake sales will probably not be materially affected by a new president, but you get my point: When a seismic news event occurs, an avalanche of commentary soon follows on how, in this case, a Trump presidency will impact every nook and cranny of society.
Rather than speculate in those areas, the focus of this post will be to view Trump’s victory through a publicity lens. Is there a “teachable moment” for the marketing and public relations industry given the uniqueness of how Trump used his brand and marketed himself? What does his victory say about the value of the estimated millions upon millions of dollars in “free” earned media coverage national and local media lavished upon him for several months, reducing his need to spend on traditional TV, radio, print and online advertising?
Depending on which way you bend politically, each person will no doubt have their own opinion on why Trump won. Either way, ad and marketing agencies across the country are re-evaluating what they know and thought they knew about consumers in the wake of the election results. An article in today’s Wall Street Journal cites how ad giant McCann Worldgroup assembled top execs to dissect what Trump’s victory means from an advertising perspective. The broader article theme postulates on whether brands have overlooked the same rural voters who fell under the big data and polling radar to propel Trump in key battleground states.
The uniqueness of the presidential campaign offers some insights for marketing, advertising and PR agencies wondering if consumer behavior will match voter behavior in the coming months and years.
Modesty doesn’t always sell
Imagining how and why Trump’s message resonated with so many people harkens me to a person watching infomercials at 3am. Deep down, you know that the BackMassage 3000 can’t possibly cure your back pain in five minutes or less, but its three o’clock in the goddamn morning. You’re tired, and everything else you’ve tried hasn’t worked, so why not give it a chance?
Trump as a brand was not modest about what he thought he could accomplish during the campaign, and the results suggest many voters responded favorably to his ambitious promises. Perhaps some knew deep down that he wasn’t going to be able to deliver on all of it, but like the BackMassage 3000, it sounded bigger and bolder than anything they heard before.
Jargon can obscure the brand promise
As an acronym, keep it simple stupid (KISS) has been applied to endless use cases, from politics to sports to sales. KISS traces back to a U.S. Navy design principle in the 1960s, and has served as a reminder to avoid adding unnecessary complexity. Trump kept his messages very simple; and these messages were either embraced or reviled by voters because the messages were easy to understand. Brands often complicate the product message with jargon that may be technically accurate, but falls flat when it comes to establishing a connection with everyday users.
It pays to be memorable
And then there was one. The Republican party began the 2016 presidential campaign with 17 candidates. My bet is that if voters were asked to describe 1-2 unique ideas that the other candidates had – whether it was Scott Walker, Marco Rubio, Rick Perry or Jeb Bush – they’d be scratching their heads for quite some time.
Think about the commoditization of budget to mid-level hotel chains, who typically offered similar rooms, at similar prices, with similar amenities. How does a traveler pick one over the other? It can often come down to creating some calling card that is memorable. For Hampton Inn, it was the Belgian waffles at the free breakfast buffet. Guests remembered the Belgian Waffles, and returned to Hampton Inn just for the breakfast.
Trump marketed campaign promises that were very, very different from other candidates, which made these promises memorable and, by default, Trump memorable with voters struggling to figure out how each of the 17 candidates was difference from one another.
You can’t build a brand overnight
One of the most overlooked but critical elements of Trump’s success is that he had spent decades building an oversized brand that could be immediately activated for his campaign. This was critical, because while 17 candidates on the GOP sides sounds like a lot, many ran out of time and money to develop brand awareness – not only around who they were but what they represent. For every Jeb Bush and Chris Christie entering the fray with baseline brand awareness, there was a Bobby Jindal, George Pataki, Scott Walker and Jim Gilmore – folks known inside the beltway but certainly not to most Americans. Trump came in with an established brand known to probably most every single voter, and the media fed this brand throughout the campaign with free publicity that negated his need to advertise heavily or introduce himself to voters.
Big data has its limits
Marketers and advertisers are stepped in big data today, but the previously referenced WSJ article makes another good point: Big data may not be telling them everything they need to know, and if this data skips over important source blocks such as rural voters, then it is by default flawed data. Finally, if the data misses key demographic segments, brands might make assumptions about who their customers aspire to be. Rural voters may not aspire to have the latest iPhone that celebrities and athletes use, but may just want reliable phone and data service that can be hard to come by in rural areas.
Will Donald make sales of Red Velvet cupcakes great again? Only time will tell.
The marketing and communications business is at a bewildering junction, with two simultaneous models vying for brains and assets. Most marketing campaigns look at personas of their buyers and determine what is the best path to the promise land.
Bottom-up marketing is a concept with no single definition, but a few distinct components that set it apart from traditional top-down marketing strategies. Unlike traditional marketing, where executives create a marketing plan and a strategy to promote a company’s products and services, bottom-up marketing is mainly driven by the employees of a company. Employees recognize one specific customer need the company can meet and create a marketing strategy around that single idea.
A great example is Dropbox. Dropbox rose to $10 Billion valuation through its connection with the end user. Dropbox focused on providing the masses of end users (both personal and professional) a block of cloud storage that elegantly and brilliantly stayed synchronized on your local hard drive and your collaborative peers hard drives. Dropbox didn’t sell the CFO on cost benefits and the CTO on the power of the cloud. Dropbox simply delivered a great service with a viral approach to a roll out that created an ever growing desire for more and more storage in the cloud. In the end so many businesses had hundreds and thousands of BYOS (bring your own storage) and they needed to take control of this corporate intellectual property, and reached out to Dropbox for the suite of tools and administration to make managing the cloud instances so much more manageable, secure, and scale-able.
The top-down marketing plan contains four principal sections: situation analysis, marketing objectives, marketing strategy, and tactics. A company’s marketing objectives should be logical deductions from an analysis of its current situation, its prediction of future trends, and its understanding of corporate objectives. In the end, a top down marketing approach focuses on the top executive personas most often. The constituent who controls the purse strings. All SaaS and Enterprise technology companies are always looking for the high and mighty inside an enterprise that has the power to sign on the dotted line. Top down marketing focuses its message and offers so they should relate to the needs of specific target markets and specify sales objectives. Marketing-target objectives should be specific, quantitative, and realistic. The messaging of a top down approach often caters to the fears and dreams of that influential executive.
A great example of top-down marketing is the hyper growth industry of cyber-security. Every executive fears waking up to their employer’s brand on the headlines of major media outlets next to the word breach or hacked. Years and years of customer loyalty and brand preference can be washed away overnight. Cyber security companies are preying on these executives with a top down marketing approach that strikes fear into their hearts and minds and forces them to strike the check and implement countless solutions to help them sleep easy at night as they try to appease key constituencies including public markets.
Does your business ever wonder how to harness its precious marketing and communications budget to achieve its short and long term goals? Contact Bluetext. We are a top marketing agency that delivers results whether your campaign is focused top down or bottom up. Let us use our proprietary methodologies to define the right method, and then develop the campaigns, platforms, and content assets to knock the cover off the ball.

With competitive global markets, what makes your brand different from your competitors?
Sometimes, it takes market research to identify what makes you unique and what’s really important to your target customers. Fill out the form to download Bluetext’s Market Research Primer so you can understand how to:
- Leverage research to craft a market message
- Develop a positioning strategy
- Stand out from the crowd
Download the Market Research Primer to get ahead of the competition here!
At Bluetext, we are frequently approached by organizations who are questioning the strength and positioning of their brand. They sometimes feel that their brand is getting stale, or that their service and solutions offerings no longer match up to the original name and are looking for guidance on what they should do. This is never an easy question. Any brand that has been in a market has built up brand equity and has begun to stand for something. Target audiences, including current customers, prospects, employees, partners, industry analysts and influencers, have perceptions of the brand, an image in their heads about its people, what the company can deliver, the quality of its products, solutions and services and whether they want to do business with the organization.
Knowing if and when to update the brand, through a new look and feel, a refreshed logo or tag line, its messaging and even its name, is important. We talked with a large company recently that was the market leader in their key verticals. Yet they didn’t think that their legacy brand and name would take them where they wanted to go, and wanted our counsel. Making the decision to jettison a name for a company in a leadership is a huge commitment and one that should never be taken lightly.
The answer is often found in market research in the form of a carefully crafted survey that will uncover what customers and prospects know about the brand, feel about the brand and how they would be likely to react if that brand underwent significant changes. It might be that a simple brand refresh is the best move, modernizing the logo and look and feel, for example. In other cases, a whole new name and approach to the market might be what’s needed to move the company to the next level. In every case, that decision should be informed by real insights into the market, and not just gut feelings that executives might have, no matter how close they think they are to their customers.
By surveying customers about a brand, the goal is to gain insight into very specific areas of knowledge and associations. This means that the survey approach has to be deliberate and precise. When done right, a brand awareness survey can offer the needed insights into:
Brand Recall: With brand recall, the respondent is given what’s known in the trade as an “unaided” question about which brands come to mind when, for example, they think about that particular market or solution. No options are provided to select from.
Brand Recognition: This is the “aided” opposite of an “unaided” question. The respondents are provided a list of companies with the goal of understanding when presented with a list of brands, do they recognize the company as a reputable option.
Brand Identity: Brand identity seeks to test which attributes the respondents associate with the company, and to understand how effective the marketing efforts have been in presenting the brand to the audience.
Brand Image: A brand’s image is based on the customer’s perception alone. Tracking disparities in the marketing and the image can reveal important gaps in marketing campaigns and results.
Brand Trust: This a fairly direct question that measures whether your audiences feel the brand is trustworthy, and is important for understanding client retention trends as well as new client acquisition.
Brand Loyalty: Loyal customers are often the best way to win over new ones, so tracking loyalty can give insight to whether the company is building the kind of customer relationships that turn them into evangelists for the brand.
Customer Profile: Changes in your core customer base may signal the need for a pivot, either in the product or service or in the marketing.
We are big believers in market research to inform these types of high-risk decisions, but only if it is the right kind of research that will deliver the insights that are needed. Not every research tool is going to deliver the best results for the client. Bluetext employs a number of methodologies for understanding how a market perceives a brand. They fall into a family of four types of survey tools and strategies, each providing a different way to reach a target audience and each that will deliver different types of insights:
IDI’s—In-Depth-Interviews are an easy way to understand the perspectives of the company’s executives as well as key customers. They are typically done one-on-one and follow a guided set of questions in order to compare answers among executives. They are conversational in order to get into more depth than a multiple choice question on a survey. We recommend including the CEO and head of sales as well as board members, customers and partners.
IDI’s help set a baseline from those with the most knowledge of the company and the market. They also allows us to gain insights from those on the front lines with clients and prospects, and how those key decision makers react and respond to the brand’s messaging. What IDI’s don’t do is give an unbiased view of the company, because by definition they rely on those with the most knowledge of the company. We think that is very valuable when beginning any research project. We use IDI’s extensively as part of our Discovery process and to develop new messages.
Online Panel Surveys—Online panels are today’s version of the phone surveys that used to dominate the research field, and understanding the difference is important. Panel surveys are gathered from people who agree to be included in online surveys, and are broad enough to provide a random sample for statistical purposes. One of the main differences from phone surveys is that the audience is self-selecting: they agree in advance to be included in panels.
Phone surveys have gone out of favor for our purposes due to the shrinking demographics of households that have phone lines, legal restrictions on calls to cell phones, high cost and declining participation rates. While phones surveys are important when a very precise analysis of public attitudes is needed, such as political campaigns, for example, we rarely include these in our clients’ projects.
Online panel surveys deliver a broad section of the target market with a randomized sampling that enables projections within a margin of error, and are the most economical way to do that. Online panels will include individuals who may not have a direct knowledge of the company or brand at issue, and so may provide insight into how well a brand is known compared to its competitors. However, those same individuals won’t have any insights to a company with which they are unfamiliar. For that reason, these types of surveys make the most sense when the company has enough name recognition or a large enough footprint that a majority of the survey respondents would have a good likelihood of at least some recognition of the company. We also recommend online panel surveys to understand market trends, audience behavior and to generate news or content in the form of proof points or even surprising results that challenge conventional wisdom.
Database Surveys—When the goal is analyzing how a company’s market and ecosystem perceives that brand, for example in relation to its key competitors, relying on people who already have familiarity with the company can often deliver the best results. This is especially true for brands that may not be a house-hold name in that market, and thus the majority of respondents to an online panel survey would not know the company. In these situations, we often recommend leveraging the company’s own database, which typically includes current and past customers and clients, prospects and others with whom they have communicated with or marketed to previously. By definition, this audience will have at least some familiarity with the brand, either through direct experience or through receiving emails or being targeted in marketing campaigns.
We call this approach “database surveys.” This allows us to employ a method that is more cost effective while still obtaining the valuable insight the company needs to make the hard brand decisions. The cost savings come in not having to purchase an online panel list or survey tool. We can employ survey tools like Survey Monkey to compile the responses and parse the data.
Focus Groups—The fourth tool that we use is called a Focus Group, which is a conversation with up to a dozen people at one time, led by a moderator who guides the discussion. Focus groups can use recruited individuals who fit certain categories, such as the industry they work in, the rank in their company, and even demographics for age and location. They can also use members of the company or customers, much as the IDI’s do. Focus groups are not randomly selected and do not return statistically significant responses, but that is not their purpose. They are better suited for testing new messaging, getting a response to a new brand or look and feel, or diving more deeply into perceptions and biases. One challenge of a focus group is that a particular individual can dominate the discussion and limit the participation from others, but a good moderator can keep the group on track and the conversation productive.
If you feel that your brand isn’t performing up to expectations, or believe it may be time for a refresh or a new direction, gives us a call. Bluetext can craft the right approach that will deliver the insights and results to make the right decisions.
In the competitive government market, what makes your brand different from your competitors?
Sometimes it takes market research to identify what makes you unique and what’s really important to your target customers. Fill out the form to download Bluetext’s Market Research Primer so you can understand how to:
- Leverage research to craft a market message
- Develop a positioning strategy
- Stand out from the crowd
To download our Market Research Primer, click here!
In the competitive non-profit world, what makes your brand different from your competitors?
Sometimes it takes market research to identify what makes you unique and what’s really important to your target members. Fill out the form to download Bluetext’s Market Research Primer so you can understand how to:
- Leverage research to craft a market message
- Develop a positioning strategy
- Stand out from the crowd
Download the Market Research Primer here!
