Marketing government contractor services requires a distinct approach. With federal, state, and local agencies carefully vetting their vendors, competition is fierce, and standing out is essential. Success hinges on developing messaging that conveys value, trust, and alignment with government priorities. This blog explores the strategies and insights needed to craft a winning message for government buyers.
Understanding the Government Buyer
Key Challenges Government Buyers Face
Government buyers often operate under tight budget constraints, face complex procurement processes, and must adhere to strict compliance requirements. These challenges demand that contractors offer not just products or services but solutions that simplify and enhance their operations.
Priorities of Government Buyers
Government agencies prioritize cost-effectiveness, risk mitigation, and mission-critical outcomes. Contractors who understand these priorities and craft their messaging to address them will stand out in a crowded market.
Tailoring Messaging to Align with Their Needs
- Emphasizing Cost-Effectiveness: Showcase your ability to maximize taxpayer value.
- Highlighting Reliability and Proven Success: Provide evidence of consistent performance and successful project delivery.
- Communicating Alignment with Agency Goals: Demonstrate an understanding of specific agency missions and how your services support their objectives.
The Foundation of a Winning Message
Clarity and Simplicity
Government buyers need to quickly grasp the value of your offerings. Avoid technical jargon and present your value proposition in clear, concise terms that resonate with decision-makers.
Focus on Outcomes
Rather than emphasizing features, shift the narrative to benefits and measurable results. For instance, highlight how your solution improves operational efficiency, reduces costs, or enhances security.
Proof of Credibility
Trust is paramount in government contracting. Showcase certifications, past performance, case studies, and partnerships with other agencies to establish your credibility and expertise.
Crafting Value-Driven Messaging
1. Highlight Cost-Effectiveness
Government agencies must justify their spending to taxpayers. Position your services as a cost-effective choice by showcasing ROI, long-term savings, and value-added benefits.
2. Address Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Compliance is a top concern. Emphasize your adherence to relevant regulations such as FAR/DFAR and explain how your services reduce operational, financial, or security risks.
3. Align with Mission Goals
Every government agency has a unique mission. Tailor your messaging to demonstrate how your offerings directly contribute to achieving their objectives. For instance, when marketing to FEMA, emphasize capabilities related to disaster response and recovery.
Strategies for Multi-Tiered Messaging
Federal Agencies
Federal agencies often require scalable and innovative solutions that can support large-scale operations. Messaging should focus on your ability to handle complexity and deliver results at scale.
State Agencies
State agencies value regional expertise and the ability to address local challenges. Highlight your familiarity with regional needs and the community impact of your services.
Local Agencies
For local agencies, responsiveness and personalized service are key differentiators. Emphasize your ability to provide tailored solutions and swift support.
Channels for Amplifying Your Message
Direct Outreach
Engage decision-makers through targeted emails, government-specific events, and one-on-one meetings to build strong relationships.
Digital Marketing
Optimize your online presence with paid media, SEO targeting government procurement keywords, and LinkedIn campaigns aimed at government audiences.
Content Marketing
Publish blogs, white papers, and thought leadership pieces that address pain points in the industry. This positions your brand as a trusted advisor and expert.
The Metrics of Success
Tracking RFP Conversion Rates
Measure how many RFP responses convert into contracts to evaluate the effectiveness of your messaging.
Monitoring Engagement Metrics
Analyze digital campaign performance, including clicks, shares, and inquiries from government audiences.
Client Feedback
Gather input from agency clients to refine your messaging and better address their evolving needs.
The Art of Messaging for Government Contractors
Crafting a winning message requires a deep understanding of government buyers, a focus on value-driven outcomes, and clear communication of your unique advantages. By aligning your messaging with the priorities of federal, state, and local agencies, you can maximize your competitive edge and build lasting relationships.
In today’s digital age, data-driven marketing has become essential for businesses to thrive, enabling brands to tailor their messaging, predict customer needs, and enhance client experiences. For the financial services industry, however, data-driven marketing is both an opportunity and a challenge. While leveraging data can lead to improved customer engagement and retention, financial services firms operate in one of the most heavily regulated industries, with strict data protection and privacy guidelines that must be meticulously followed.
To succeed, financial marketers must adopt data-driven strategies that respect compliance standards, ensuring that all customer data usage aligns with regulatory expectations. This blog explores strategies for harnessing the power of data analytics in a way that enhances marketing efforts while staying within the bounds of regulatory compliance.
The Benefits of Data-Driven Marketing in Financial Services
Data-driven marketing is invaluable for financial services firms aiming to connect meaningfully with their audience. Here are key benefits that data can bring to this industry:
- Personalization
Data allows marketers to go beyond basic customer information, enabling hyper-targeted, personalized messaging based on individual preferences and behaviors. For financial services, this means delivering customized product recommendations, financial planning advice, or educational content that aligns with each client’s unique financial goals. - Predictive Insights
Predictive analytics uses historical data and trends to anticipate future customer needs. For example, by analyzing a client’s transaction history, firms can predict significant financial milestones, like retirement planning, and proactively offer relevant services. Predictive insights enhance the client experience, positioning the firm as a proactive advisor rather than a reactive service provider. - Enhanced Customer Retention
Retaining customers is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones, and data analytics plays a crucial role in fostering loyalty. By tracking client interactions and satisfaction metrics, firms can identify at-risk clients and develop strategies to re-engage them through timely, targeted communication.
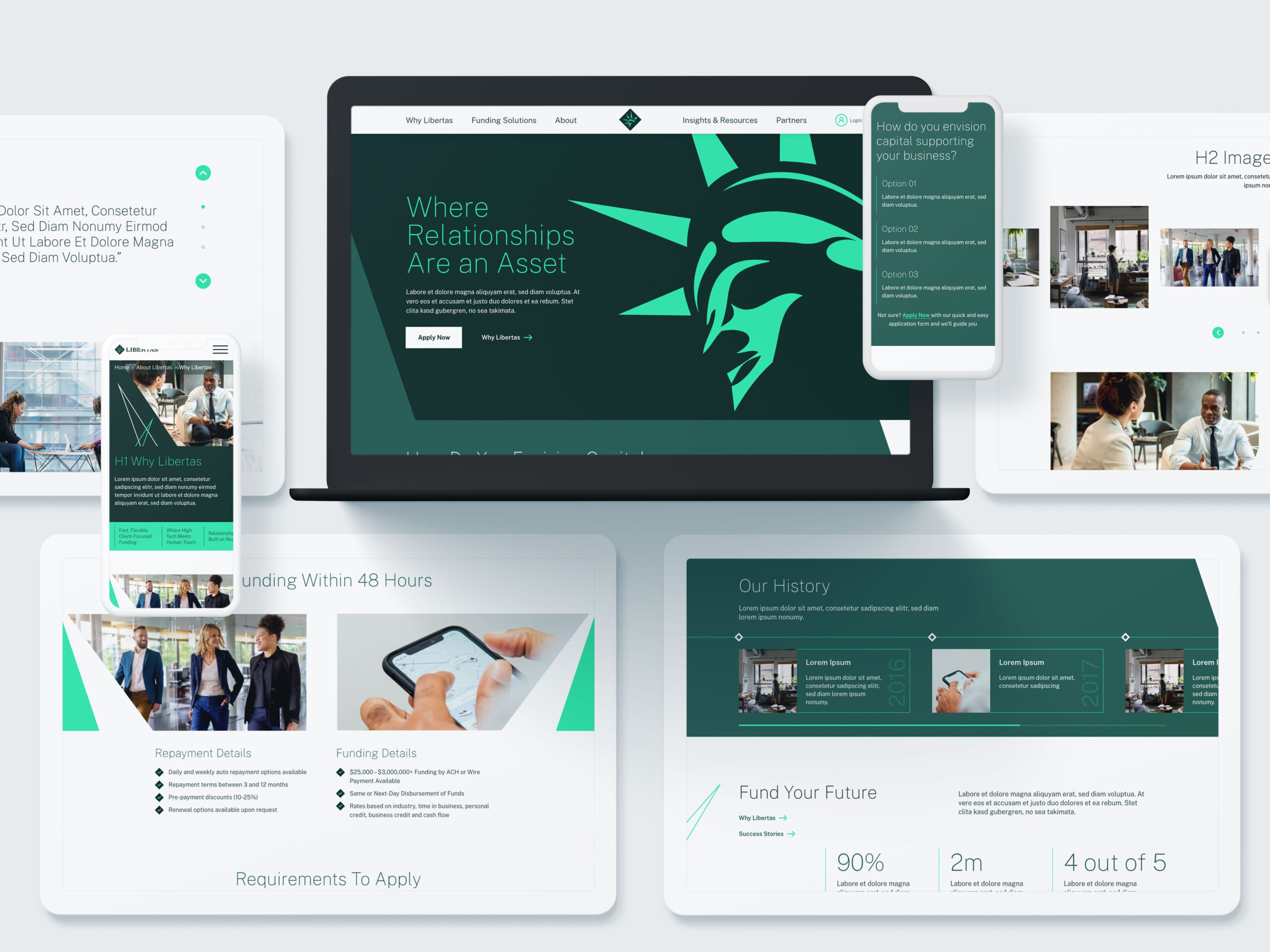
Navigating Regulatory Challenges
In a heavily regulated environment, financial services marketers must exercise caution in how they collect, process, and use customer data. Key regulations governing data privacy include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Applies to firms handling the data of European Union residents and mandates strict guidelines on data consent, access, and usage.
- FINRA Compliance: Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) oversees financial firms to ensure ethical practices, including marketing communications.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Grants California residents rights over their data and applies to firms collecting data on California residents.
A compliance-focused approach to data is essential for financial services. This means establishing transparent data practices, securing explicit consent from customers, and adopting a culture of privacy by design. Additionally, regular audits are essential to ensure that data management practices align with evolving regulatory requirements.

Key Data-Driven Marketing Strategies
Balancing regulatory constraints with effective data use can be challenging, but the following strategies allow financial marketers to harness the benefits of data analytics responsibly:
- Segmentation and Targeting
Using segmentation, financial firms can divide their audience into groups based on attributes like age, income, or account activity. Segmentation enables marketers to send targeted messages tailored to each group’s unique needs, improving campaign relevance and client engagement. - Omnichannel Personalization
Today’s customers interact across multiple channels—from social media to email to mobile apps. Omnichannel personalization ensures clients receive consistent, seamless experiences across platforms. For example, a customer viewing investment advice on your website might later receive a relevant email newsletter with complementary financial resources. - Predictive Analytics for Customer Lifecycle Management
Predictive analytics helps firms anticipate key moments in a customer’s lifecycle, such as significant life events or investment milestones. By identifying these opportunities, marketers can deliver timely offers or educational resources that address each client’s evolving needs, leading to stronger client relationships and higher lifetime value. - Data Quality and Security Measures
Data integrity is critical, especially in regulated industries. Implementing robust data quality measures—such as regular cleansing, validation, and secure storage protocols—ensures that the insights driving your marketing are both accurate and compliant. Utilizing secure platforms and encryption methods further safeguards client data, building trust and compliance with privacy laws.
Steps to Implement Data-Driven Marketing Safely
Implementing a data-driven strategy in a regulated world requires careful planning and coordination. Here are actionable steps to help financial firms adopt data-driven marketing safely:
- Build a Cross-Functional Team
Effective data-driven marketing requires collaboration between marketing, compliance, IT, and legal departments. By creating a cross-functional team, firms can ensure that campaigns are both innovative and compliant, benefiting from diverse expertise to navigate complex regulations. - Invest in Secure Data Infrastructure
Security is paramount when handling sensitive financial data. Investing in a secure data infrastructure, including advanced analytics platforms and encryption technology, protects client information and helps your firm meet regulatory requirements. Leading platforms offer built-in compliance tools, streamlining the process of adhering to data protection standards. - Develop Clear Data Governance Policies
Establishing clear policies on data collection, usage, and retention ensures that all employees understand the boundaries of data-driven marketing. Policies should include guidelines on obtaining consent, using data responsibly, and securely storing client information. Regular training and policy reviews help keep the team informed and compliant with any regulatory updates.

Embracing Data-Driven Marketing in a Regulated Landscape
Data-driven marketing offers financial services firms a powerful advantage in understanding and engaging clients more effectively. By focusing on customer segmentation, predictive analytics, and omnichannel personalization, firms can enhance their marketing while respecting the industry’s stringent regulatory standards. With careful planning and a commitment to compliance, financial firms can leverage data to build stronger client relationships, improve retention, and drive growth.
Looking to integrate data-driven marketing into your strategy? Contact Bluetext today for expert guidance on implementing effective, compliant data practices tailored to the financial services industry.
Maybe you’ve seen one of those large banners across your Google Analytics property: “Universal Analytics will no longer process new data in standard properties beginning July 1st, 2023. Prepare now by setting up and switching over to a Google Analytics 4 property.” Seems problematic, right? Such a warning rings an alarm and raises several good questions to digital marketers, including: What is GA4? Should I switch now? Why is Google making me change? How do I switch? Will I still be able to access my data from previous years? If your mind is buzzing with these questions about your marketing analytics data you’re not alone. Luckily Bluetext has done its research and is here to answer some frequently asked questions and quell any lingering fears over this transition. This article will empower you to make an informed decision about Google Analytics 4.
Schedule a consultation today.
What are Universal Analytics and Google Analytics 4?
Universal Analytics (UA) is Google’s third iteration of its popular web analytics service. If you’ve logged on to Google Analytics in the past decade, you were more likely than not using UA. When UA launched in 2012, it was quite a technological leap, adding advanced features in cross-platform tracking and custom dimensions. It shaped Google Analytics from simply being a page view tracking platform to a robust data reporting and attribution tool that could compete against some of the largest web-oriented business intelligence platforms, like Tealium. Most importantly, Google provided nearly the whole feature set free of charge.
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is simply Google’s newest iteration – think of it as a new generation of analytics technologies. The web has transformed significantly since the early 2010s, and Google is merely re-platforming analytics to match today’s realities. GA4 launched in 2019 to little fanfare but only recently gained significant traction in March of this year due to Google’s landmark announcement that GA4 will be the only analytics service it supports in 2023.
Why is Google Switching to Google Analytics 4 and Ending Support for Universal Analytics?
This is a complex question – with some good answers that Google will give you and some answers you’ll need to read between the lines to get. Google’s official statement is that GA4 better reflects the modern web. UA did a woeful job reporting on non-webpage-based metrics, such as those from web apps. It was also cumbersome if your reporting needs didn’t precisely match those of a traditional website experience – e.g., single-page or non-linear web apps. GA4 is more customizable and reflects modern data collection and attribution processes better.
The underlying message here, though, is that of data privacy. Since UA launched nearly ten years ago, fundamental shifts have occurred over how people and the law treat data privacy on the web. Think of Edward Snowden, GDPR, and the countless data breaches over the last decade. At its core, Google realizes that this enormous cache of web data collected from millions of websites, even if not strictly Personally Identifiable Information (PII), is a huge security risk to the company. GA4 is an attempt to offset some of that risk, either removing entirely or at least offloading it to individual companies. GA4’s data collection methods are more anonymized, and data retention is limited to 14 months. Overall, this is a calculated move by Google to push its analytics customers to use tools that won’t put Google in hot water.
What’s similar between Google Analytics 4 and Universal Analytics? What’s different?
While the actual end-user experience may look starkly dissimilar, the foundation remains the same. GA4 will remain an incredibly flexible web analytics platform suitable for most websites today – regardless of whether it’s a personal blog, an online retailer, or a corporate website. Most day-to-day tasks like page view tracking, user attribution, and measuring bounce rates will remain the same. GA4 merely stores these metrics and measurements in alternative locations.
That isn’t to say everything is identical. The significant differences you’ll notice every day are rooted in the architectural shift in hit types. UA treated things like page views, events, and e-commerce tracking as separate entities or “hit types.” GA4, on the other hand, treats them all as “events”. Any tracking item will now be an event: resource downloads, page scroll, form submits. Google is thus simplifying the old event architecture by putting everything on the same level – everything is an event with associated customizable event parameters.
For example, under UA, a resource download event might have looked something like this:
- Event Category: Downloads
- Event Action: Resource Download
- Event Label: resource_file_name.doc
- Event Action: Resource Download
Note that regardless of whether it was necessary, Events always took on this three-stage hierarchy. GA4 removes this rigid hierarchy. Instead of having the arbitrary “Event Action” and “Event Category” dimensions, GA4 lets one create as many custom event parameters as necessary to communicate an event’s nature fully. GA4 can track the event instead as:
- Event: Download
- Download Type: Resource
- File Name: resource_file_name.doc
Sessions are also changing. By default, UA defined the end of a session by identifying 30 minutes of inactivity since the last event. GA4 measures the period between the first and last events in a session. GA4 also doesn’t create a new session when a user’s campaign parameters are changed. The major takeaway of these changes is that session numbers will likely be lower in GA4 than in UA.
Aside from these two critical areas, there are many other minor changes. While lesser in scope, these changes may affect your reporting, depending on what kind of features you currently rely upon regularly. For example, customizable views for properties are going away in GA4. If you depend on different views, you’ll likely have to experiment with custom audience building to replicate the reporting. As mentioned before, GA4 will also only store data from the previous 14 months.
Documenting every change is beyond the scope of this blog post. If interested in getting into the nitty-gritty, read through Google’s documentation on the significant changes.
Do I Need to Switch to Google Analytics 4?
Google states that no further data will be processed after July 1st, 2023 (Customers of 360 Universal Analytics get a small extension to October 1st, 2023). While Google may extend to a further date, make no mistake, Universal Analytics will eventually be completely deprecated. If your business relies on web analytics in any form, you need to start planning soon on what your migration plan looks like – hopefully well before July of next year.
How Can I Switch to Google Analytics 4?
For most websites, merely enabling dual tracking will be sufficient. Google has made an easy setup wizard for GA4. To access it, go to the admin panel for your UA property and click the “GA4 Setup Assistant” link. You can follow Google’s instructions here, but within a few clicks, you’ll have a tracking setup that collects both UA and GA4 data. You’ll already have nearly a year’s worth of GA4 data to review once UA goes offline next year. As noted previously, be aware that no historical data will be present in GA4, even if you use this wizard. That said, it will give an excellent basis of comparison to see the reporting differences, especially as you can compare each month between GA4 and UA up until the cutoff date.
Custom events and e-commerce will require a more personalized and custom approach. We’ll cover these in future guides here at Bluetext, but for now, you can consult Google’s guides on the matter here.
I hope this guide relieved some worries and cleared up some unknowns regarding Universal Analytics and GA4. There’s a lot to cover about GA4, and this guide only covers the surface. If you have any further questions about UA4 and GA4, be it migrating data, specific differences, or a transition plan, contact us to learn more about Bluetext’s analytics capabilities.
With 2022 already in full swing, companies are faced with the challenge of looking ahead to what the future might bring. Enlisting the help of a digital marketing agency like Bluetext can ensure that your company is not just reacting to trends, but thoughtfully adapting to the best practices in marketing and staying ahead of the curve. Here are 6 key predictions on how brands will bolster their marketing efforts in 2022:
1. Selling Your Brand, Not Your Product
The importance of brand recognition is nothing new, but the significance of strong brand identity will continue to increase. The modern-day user is inclined to invest in the companies they want to support, not just the products they want to buy. Especially in saturated markets, such as cybersecurity and technology, there are a million and one companies that sell the same or similar products. The skill of storytelling will be imperative in this upcoming year as firms will need to convey strong brand identity and powerful messaging to capture customers. Hiring a marketing firm could help your brand tell its story with seasoned marketing expertise. A consistent messaging strategy or compelling video content crafted by marketing professionals could be what sets your brand apart. Bluetext has a growing portfolio of brand videos that showcase how media can be used to create granular, compelling content to best tell your story to the market.
2. Being Prepared for Change in the B2B Sector
The B2B landscape in marketing is rapidly changing as a result of long-term disruptions caused by the global pandemic. As remote work has become a more permanent reality for many businesses, the reduction of in-person interactions is causing a shift in lead-generation strategies for B2B marketers. A digital and mobile-first marketing approach is more important than ever before, as many B2B buyers prefer remote interactions rather than personal experiences with sellers. In-person events are now mostly hosted in online environments instead, which have brought challenges to traditional lead generation. To remedy this, more B2B companies are capitalizing on social media as an important lead generation channel. A leading social media marketing agency like Bluetext can provide strategic and creative communications that engage with corporate customers through the most effective online touchpoints.

3. Responding to Increased Sensitivity to Marketing
Public awareness has become increasingly attuned to issues of diversity, equity, and inclusion. As companies are competing for attention in this space, firms can use marketing techniques to promote their core values while supporting the causes they stand for. This will help to gain trust and respect from customers who are expecting brands to be active in their communities.

4. Preparing for Marketing to Become Tougher
As consumer behaviors and privacy policies change, the platforms that host advertisements are changing as well, which creates challenges for marketers to navigate these spaces. Increasing regard for customer privacy will continue to make it difficult to obtain data and insights from online campaigns. In addition, platforms are updating their algorithms to respond to market changes, leaving advertisers to adapt to their new preferences. For example, Google’s changes in SEO ranking and Instagram’s shift to prioritize video content have already created challenges for marketing efforts in 2022. Businesses should expect to continue seeing these sorts of shifts, and be proactive in utilizing these platforms. Getting ahead of these changes and pivoting campaign strategies will accelerate prepared companies to becoming frontrunners of their pack.
5. Teaching Rather than Selling
One of the most important ways a company can gain respect from their audiences in 2022 is by addressing topics that are top of mind in their industry. Focusing your online presence on content marketing can help promote your brand’s expertise without explicitly advertising competitive advantages or product details. In the coming year, companies should be working to share more thought leadership pieces like blogs, whitepapers, and video content to bolster their online brand and increase their search ranking.

6. Utilizing AI/ML
Effective digital marketing campaigns must continue to utilize emerging technologies, one of the greatest tools in 2022 being artificial intelligence. Machine learning can ensure the productivity and effectiveness of your marketing efforts. You can bolster performance by accurately tracking KPIs and budgeting, while also personalizing and optimizing digital ad campaigns. Harnessing the power of machine learning applied to brand marketing will be a necessary skill for companies looking to thrive in 2022.
You may already be aware of these trends and the implications they could have for your business but unsure of how to start addressing them. Bluetext has the expertise and industry experience to help you grow your brand and implement effective changes to your marketing strategy. To learn more about our offerings, contact us today.
Data privacy features can be overwhelming. Every time you visit a new site, you’re immediately prompted with the same spiel: “Hey! Is it okay if we take your data?” You probably click ‘yes’ just to get rid of the annoying pop-up.
But what happens when you click yes? How are publishers using your data? How are we — the consumer AND the advertiser — affected by these data protection policies?

Understanding Data Protection Policies
Data protection policies really started to emerge and take force in the past several years. The most widely known data protection policy is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which was implemented in 2018. GDPR, in short, is “a legal framework that sets guidelines for the collection and processing of personal information from individuals who live in the European Union.” You can learn all about GDPR and what exactly the regulation covers on the official GDPR site.
But say you are an American-based company, are you affected by data privacy regulations? Just months after GDPR was enforced, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) was launched. Similar to GDPR, “CCPA outlines how businesses can collect, store and transfer consumer data from Californian residents.” You can find out more about what the Act covers on the official CCPA site.
The launch of these two acts threw many users and advertisers for a loop. For starters, if users are visiting your site from California or Europe, your site must be compliant. And let’s not forget one of the hallmarks of the “worldwide web” — the ability to connect users across physical boundaries. Remember the pop-up boxes and prompts we talked about earlier? Those were implemented across sites based on these new data privacy laws. In order for websites to be compliant, there has to be an explicit opt-in consent message that appears as soon as users visit a site, and no data can be collected unless the end-user opts in. This is a change from traditional advertising regulations in America, which required the option to opt-out (does the “unsubscribe” button sound familiar?). If a company fails to comply with these policies, it could “face a fine. In most serious cases, this fine could be up to 17 million euros or 4% of a company’s annual turnover.”
Data privacy acts are no joke! It’s imperative that companies follow the correct guidelines to ensure sites remain compliant — both for the company’s sake and the consumer’s sake.

What Consumers Should Consider
The next time you are prompted with a consent message, just remember: if you click ‘yes,’ you are giving that company permission to collect and use your data. If this sounds eerily vague and leaves you questioning what a company wants from your data, you’re not alone. We encourage users to navigate to the privacy policy pages on sites before opting in; this way, you’ll know exactly how companies will use your data if you choose to click ‘yes.’
While “collecting data” sounds like a serious invasion of privacy, it’s worth noting that most companies only scrape the surface of data — data is usually anonymized and does not reflect any personally identifiable information (PII). Most companies know the importance of building trust with their consumers, especially as data privacy is at the forefront of most digital conversations. For this reason, companies are usually transparent in their privacy policy — showcasing exactly what data will be collected — and how that data will be used. Again, when in doubt, check out the site’s privacy policy page!
Many consumers have found that checking the ‘yes’ box does have its advantages. Have you ever visited an eCommerce site, eyeing a particular product, but passed because of the price tag? Many marketers set up retargeting campaigns — which are only activated if users accept the privacy policy — that enable them to serve product ads to users who leave the site without purchasing. If you’ve opted into the privacy policy, you might start to see ads of the product you wanted to purchase (or similar), and in some cases, a nice discount code will appear with the ad! In many cases, customers value the reminder to checkout their online cart and especially enjoy saving money in the process.
Another less obvious example is user experience. Websites will use consumer data to help create a more seamless experience for the end-user by understanding what the user is most interested in. We say this is ‘less obvious’ because when done right, you might think that the website is answering all your questions and solving your problems intuitively. Maybe it is — or maybe it’s the data talking.

How Advertisers Should Navigate
As mentioned above, when it comes to data privacy and data protection policies, advertisers should prioritize consumers’ safety. In order to establish yourself as a trustworthy brand or company, make sure that you’re complying with all data regulations and are transparent with users about how their information is collected and used.
As long as you’re complying with data protection laws, you still have the same targeting capabilities. Here are some ways of leveraging data to build your brand’s digital presence:
- Create retargeting lists across platforms to follow-up with users who visited the site but didn’t convert, placing a more targeted ad in front of those end-users.
- Leverage compliant 1st party data to inform content development, predictive analytics, addressable advertising, and more.
- Learn and improve your site based on analytics data. If one of your most-visited landing pages has a high bounce rate and a low avg. time on page, work to determine why users are leaving the page, and update the UX to create a better landing page environment.
- Use the data you’ve collected from current users to reach new users who share similar digital attributes, also known as ‘lookalike audiences.’ Create lookalike audiences across paid media platforms such as Google Ads, Facebook, Twitter, and more.
The list can go on and on! But first: make sure your site is compliant, and make sure you’re putting the end user’s safety first.
Bluetext has learned a lot about data protection policies and data privacy over the years. We’re constantly adapting our site to make sure it’s up-to-date to remain compliant with data policies, ensuring consumer data is always safe. Visit our site to learn more about how we have achieved success while remaining compliant. And don’t worry, we won’t collect any data unless you’ve opted in!
When building and launching digital campaigns, many of the key determinants of success are evaluated through digital engagement measurement and tracking. However, as websites and ad-tech have evolved in recent years, so have protections and privacy policies. It’s easy to write off the need for a comprehensive privacy policy, however, this is a recipe for disaster in the age of big data regulation and enforcement. To avoid the FTC and International regulators ire, digital agencies such as Bluetext recommend taking data privacy measures that cater to the most comprehensive regulations in effect.
For businesses with users outside of the United States, being aware of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and similar legislation is an essential consideration. The GDPR has created strict provisions for EU web users’ privacy and data rights, which extends to US browsers. As global privacy legislation evolves, North American businesses that handle global users’ data must comply with current regulations and build with an eye on future compliance. Top digital marketing agencies advise and design campaigns and websites with these policies in mind to provide frictionless engagements.

What is the GDPR?
The GDPR is an extraterritorial set of provisions that updated Europe’s data protection standards. The privacy policy strengthens the protections set in 1995, adding requirements for greater transparency and disclosure to users, in addition to modernizing the “cookie law” of 2002.
The GDPR goes beyond earlier regulation, focusing on personal data protection regardless of the type of data and how companies must document user consent in a transparent fashion. These protections apply to all persons browsing within or originating from the European Union.
The term “personal data” is not synonymous with “personally identifiable information”, or PII. PII has traditionally been a legal concern for American businesses, and it refers to a more defined set of information than the GDPR model. PII does not have to be context-specific to be regulated, in contrast, the GDPR emphasizes the consumer risks of data aggregation.
My business isn’t located in Europe, why should I care?
The GDPR’s reach is far greater than the medley of privacy protections in effect across the United States. Violators of the regulations risk penalties of €20 million ($22.6 million as of writing) or 4 percent of global annual revenues for the preceding fiscal year, whichever is greater. Comprehensive legislation at the state level in the U.S. has been varied, many forward-thinking businesses are beginning to take steps to adapt their practices to comply with the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Ultimately every website will have to comply with some set of standards, so it is wise to be proactive and implement privacy protection now. Top digital marketing agencies such as Bluetext are taking steps to protect against potential violations of the CCPA and GDPR by changing cookie collection practices, recommending new data collection practices, and designing clear consent forms.

Changing privacy policies impact sites from the bottom up, starting with development and design
In a digital-first world, data is a critical component of many businesses online and offline strategies. With the implementation of the GDPR, marketers and web developers must be more diligent about what data we collect, the means by which we collect it, and how we handle sensitive information. When building or updating websites, web developers, and digital project managers should take this as an opportunity to rethink how sites can be more transparent and adopt the Privacy by Design framework.

The Privacy by Design framework highlights design-thinking approaches to development prior to launch to eliminate the need for post-hoc privacy fixes once a project is live. Solutions such as making privacy the default setting for site visitors, making privacy standards visible and open, and giving users specific privacy information notices are easy considerations to add to the development plan.
If your site is already live, consider a development sprint focused on auditing areas of potential weakness. In assessing your data hygiene, your team can look for unsafe or unnecessary modules that can be disabled, particularly those found in APIs and third-party libraries. Adtech integrations may help source leads and retarget with better precision, but validating that their pixels and tracking are in alignment with GDPR best practices is essential.
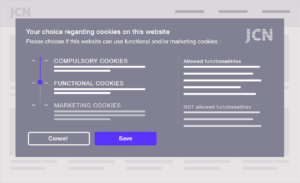
The aesthetic design of websites is also impacted by changing privacy practices. GDPR consent requires clear and explicit opt-in notices to users. Designers, user experience experts, and marketers should work collaboratively to update existing landing page components to incorporate new disclosure features. One simple mantra to internalize in the design phase? Offer accessible, clean choices around cookies and pixels.
When building clear user permissions for data capture, the GDPR requires that websites define data retention and deletion plans for all the personal data collected. Adding GDPR conscious logic to scripts at the code level of your site can save time for site custodians and business analysts alike in the future.
Updating best practices for common marketing tactics and tools
Updating the fine print on your Privacy Policy is just the first step of complying with new regulations; common marketing campaign tactics such as cookies should also be rethought through the lens of compliance. Cookies are the small data files that can be placed on users’ browsers and provide a trove of useful insight to website operators. Under the GDPR, businesses are legally liable for any activities on their sites, specifically protecting user data from third-party cookie tracking.

Many businesses use cookie tracking to better measure the impact of their marketing strategies, and they combine tracking with other user data to build user personas. While this has been an accepted practice in the past, the new regulation now requires clear permission from European users to collect this information, whether the site is for an American or French company. As noted in the impact of GDPR on design, cookie usage has to be explained on either the homepage or a second-level page on the navigation. This immediate opt-in should allow users to understand how their data is collected, the purpose of the data, and how long they are consenting to these cookies.
As a website operator, sites must withhold all cookies and trackers on your website until you have received clear and explicit user consent on each type of cookie and tracker. This consent has to be given freely, described in explicit plain language, and users must have the ability to withdraw consent. The rights of users under the GDPR are extensive — to comply, website custodians must update their privacy policies and opt-in tools.
This sounds like a lot of work, why should I care?
Ultimately, thoughtful privacy policies, development, and design provide a safeguard for both businesses and users. The GDPR gives consumers new rights to access and manage their data on digital platforms, and businesses that do not adapt to meet these regulatory requirements can face steep fines. While these changes can seem overwhelming, a top digital marketing agency such as Bluetext can guide your business through the murkiness of data privacy design and compliance.
It’s time again for our top marketing trends 2019, Bluetext’s annual look at what trends are going to drive digital marketing come the new year. In this and subsequent blog posts, we will discuss additional trends for 2019, including the public’s change of attitude towards social media platforms, and then assess what to expect next year in website design, digital marketing, branding, and public relations.
For 2019, identifying an over-arching theme that will drive a significant part of the marketing industry is not hard. Privacy, ranging from significant new regulatory requirements, massive industry failures, and changing consumer expectations, wasn’t merely a distraction (or some might say annoyance) – it was a bludgeoning that top marketers had to take repeatedly, as changes to successful digital strategies got turned on their head over and over throughout the year due to changes in privacy rules as well as blow-back against platforms that appeared to disregard privacy.
First and foremost for us marketers was the General Data Protection Regulation, better known as GDPR. The regulation, which took effect in the European Union on May 25th, is a legal framework that sets guidelines for the collection and processing of personal information of individuals within the European Union. Of course, since just about every brand either does business now in the EU or wants to do business there, it is a framework that impacts every organization that interacts with our friends across the pond.
GDPR in and of itself tells you everything you need to know about how privacy is becoming the driving force behind changes to digital marketing. In a nutshell, the regulatory framework behind GDPR places personal information back in the hands of the individual, and removes it from the control of private companies, because it requires the explicit informed consent of an individual to make their information public. There are other requirements as well in the regulation, but it essentially requires marketers at every company that does business in the EU to obtain the “opt-in” consent from their customers (and non-customers). And because few people can be expected to give that permission, it is drastically changing how marketers can use the types of behavioral data that we generally collect for marketing (and other) purposes.
Here’s how Inc.com summarized the impact of GDPR on digital marketers:
“(A) s a digital marketer, you are going to have to be transparent any time you wish to collect data on someone. You will have to communicate very clearly that you want to collect data, and explain explicitly how that data is going to be used. You then have to gain consent while also informing consumers about their right to refuse or withdraw their consent. This means that you might have to get a lot more creative when trying to convert a website visitor into a lead.”
GDPR presents some very real challenges to digital marketers, who are going to be held to a higher standard than pre-GDPR. But it’s also forcing fresh thinking and more creative strategies, and ultimately it should help build better relationships between businesses and their consumers that are built on trust and transparency.
Next in our Top Marketing Trends 2019 series: How privacy blow-back to top digital platforms is changing digital marketing.
Learn How Bluetext Can Help Navigate the Top Marketing Trends 2019!
As an agency that works with a number of cyber security clients, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has been on Bluetext’s radar for quite some time. The GDPR, which goes into effect May 25th, 2018 regulates how companies must protect the personal data of European Union citizens.
The impending deadline is not lost on U.S. multinational corporations that touch EU citizens/consumers in any way, but most of the angst has been confined to those responsible for corporate compliance, IT and security. But GDPR is highly relevant to marketers and advertisers, who must start preparing now to ensure compliance. And the stakes are enormous: fines for non-compliance could be as high as 4% of a company’s global revenues! I’m no math whiz, but any executive responsible for that kind of fine can start looking for a new job now.
Whether or not marketers will be yelling Mayday! on the May deadline day roughly eight months from now will in many ways come down to becoming fully educated on the intent of GDPR when it comes to customer data privacy, its requirements, and how to convert the compliance challenge into an opportunity.
Organizations, not just CMOs, have some ways to go towards GDPR compliance. Gartner estimated earlier this year that more than half of companies affected by the GDPR will not be in full compliance with its requirements on deadline day. In commenting on this prediction, Bart Willemsen, research director at Gartner, counters the notion that this is only an issue in the European Union.
“The GDPR will affect not only EU-based organizations, but many data controllers and processors outside the EU as well. Threats of hefty fines, as well as the increasingly empowered position of individual data subjects tilt the business case for compliance and should cause decision makers to re-evaluate measures to safely process personal data.”
For marketers specifically, the confidence level in being prepared for the GDPR is similarly low…and dropping. As of May, only 54% of businesses expected to be compliant by the deadline, per a Direct Marketing Association (DMA) survey – down from 68% when the survey was conducted just three months prior. In fact, nearly a quarter of companies had not even started preparing for GDPR, even though the law was first announced in 2012.
The challenge for CMOs will be dictated by how much transparency they need to build into their marketing processes – particularly as it relates to how customer data is handled. The less transparent, the heavier the lift it will be to not only comply with GDPR, but demonstrate this compliance. Ultimately, a core tenet of GDPR – providing citizens with “ownership of their data” and right to erase their data – runs counter to the desire by brands to deliver a superior, customized experience by retaining and analyzing as much data as possible.
Clear guidance will help alleviate those concerns for marketers and others impacted by the legislation. GDPR directs companies to keep data as long as it is necessary. How marketers define what is necessary may be different than how it is defined by citizens and EU lawmakers
At the same time, some marketers are struggling to understand if efforts to be more transparent will come back to bite them. At a Direct Marketing Association (DMA) event this past May, chairman Mark Runacus pondered whether the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) would “penalize those who are trying to be open, honest and transparent.”
DIGIDAY has one of the better summaries of what marketers and advertisers need to start paying attention to now. A few takeaways from GDPR the author focuses on include:
- The definition of personal data has been broadened to include online identifiers such as IP addresses and cookies. This could cause problems for digital marketing, given cookies are not gathered with an individual’s consent.
- Under the GDPR, advertisers must get explicit and informed consent from EU residents. This means no more of the so-called “clickwrap” forms, those lengthy contracts that millions of people sign off on without reading each day. Instead, brands must find a way to get user consent, devoid of pre-checked boxes, or attempt to get implied consent.
- The GDPR won’t just affect organizations across Europe. Any business anywhere with personal data from EU residents must abide by the reforms.
- Marketers will need to take greater responsibility when processing personal data, and ensuring that the manner in which consent was acquired from customers in the database is GDPR compliant.
Within these challenges lies an opportunity for marketers to become more transparent stewards of customer data, improve data privacy and security, and build a more trusted relationship with the customer. It won’t be easy, but starting GDPR compliance now – if you haven’t already – is critical.
Looking for a strategic marketing and communications agency? Contact us!
 The third-party cookie is under attack and may soon be a thing of the past. Microsoft recently confirmed that it was developing a new tracking technology to eclipse the cookie. The idea is to have a proprietary product that it controls across platforms allowing it, and other large players, to consolidate their power through newer tracking technologies.
The third-party cookie is under attack and may soon be a thing of the past. Microsoft recently confirmed that it was developing a new tracking technology to eclipse the cookie. The idea is to have a proprietary product that it controls across platforms allowing it, and other large players, to consolidate their power through newer tracking technologies.
That might sound like the natural progression of online marketing. After all, cookies have several challenges that critics use to argue for their demise. From a privacy stand-point, many privacy advocates see third-party cookies, the ones that marketers and advertisers use to follow individuals, as intrusive. And indeed, Microsoft and other players say they have protecting consumer privacy in mind with their new technology.
But more important from a marketing standpoint, cookies are remnants of technology designed to follow users across desktop browsers. They don’t transfer to mobile devices and platforms, let alone Xbox, PlayStations and connected television and the host of new ways consumers are accessing the Internet. An advertiser has no way of knowing, for example, if a sale came from an ad viewed on a cell phone or other device because of this limitation.
On the other side of the debate, advocates for cookies point out their benefits, including as an open source technology that has been a key element in “democratizing” the Web. The technology has allowed small publishers and bloggers to flourish, and has enabled marketers to anonymously and efficiently target consumers on the Internet.
Let me give you an example of how we use cookies for our clients’ campaigns to deliver the right kind of information to their potential customers. As part of a campaign, we often create lead-generating landing pages and microsites that contain useful information on an industry challenge for which a company has a range of solutions. A visitor might go to that site and search for white papers or other premium content on a specific challenge they are facing. By utilizing an anonymous cookie to that individual, we can serve up a series of banner ads that direct him or her to more information. If the person had gone to a page on pricing, a marketer can logically guess that this person is most likely a potential buyer and can deliver banners that are tailored to that stage of the buying process. Cookies enable this type of efficient and effective targeting to work.
As one observer recently wrote, “In clamoring for the demise of third-party cookies, privacy advocates may be urging the creation of a system that elevates proprietary tracking technology – technologies that may stifle competition and may be an even bigger privacy concern with personal data being concentrated in the hands of a few powerful corporations.”
We’re not quite that alarmist, but it is worth recognizing that third-party cookies are an important part of many of the targeted campaigns that Bluetext designs and implements for its clients. They allow companies to identify potential customers who have expressed an interest in their solutions through Web searches, and provide information and links tailored to those specific interests. This type of narrow-casting ad delivery makes targeting much more efficient, serves up information relevant rather than random to users, and provides needed revenue streams to web properties including news and information sites.
“In order to pay for a better and more expensive internet we need to continue to improve online advertising,” said Zach Coelius, CEO of automated ad buying company Triggit told AdAge. “There are only two ways we can do that: One is to make the ads more intrusive, bigger and in your face, or two, we can make them more targeted so that we no longer have so much waste with the wrong ads going to the wrong people.”
Why is this so important for marketers? First and foremost, it marks a potential trend by Microsoft and other large internet platform companies to control how individuals are tracked and followed across their browsing. That’s good for those large corporations, but not so beneficial for companies that will have to purchase or obtain that information from them. It reverses the path of “democratizing” the Internet that cookies allowed for in the first place.
So what do marketers need to do now that Microsoft is going to make it more difficult to identify and track potential customers through third-party cookies? Here are a few recommendations:
- First, cookies aren’t going away yet. There will still be a need and market for them, so don’t abandon the ship.
- Be creative! Targeted campaigns that use premium content and compelling creative will attract attention from potential buyers and customers.
- Content will still be king, and content syndication can drive key targets back to your campaign site.
- Three-part campaigns that combine digital, physical and follow-up marketing will deliver better results than a one-dimensional effort.
- Follow the trends. If the large platform players are transparent about the information they collect on your behalf and can demonstrate solid results, they may be worth a try.
- Social media sites that allow segmented targeting, like Facebook and LinkedIn, will offer strong alternatives to traditional banner ads.
- Try a little bit of everything, split test messages and creative, and refine and revise until you have the best combination to deliver the results you want.