Before Twitter, LinkedIn, search engine optimization, and mobile apps there existed an individual within many enterprises that has gone all but extinct today: The public relations director. When my own PR career started on the agency side two decades ago, our in-house client contact would often include one or more professionals exclusively focused on public relations. Yes, some corporate communications positions have endured, but over time organizations saw less value in PR specialists, and more interest in hiring multi-disciplined marketing leaders and staff for which yes, public relations was one function of the broader purview. As a result, in-house PR titles have dissolved faster than the polar ice caps as it was expected that marketing professionals would come with built-in public relations skills.
A similar scenario is being debated with digital marketing leaders, as some enterprises question whether a separate position is required, or if the CMO should be expected to lead digital marketing efforts. The conversation bubbled up in an AdWeek article last week, which chronicled the departure of Umang Shah as director of global digital marketing and innovation at Campbell Soup Company. The move was announced as the company’s CMO, Greg Shewchuk, assumed digital marketing strategy responsibilities.
Addressing the move, Campbell’s spokesperson Megan Haney told AdWeek that, “Digital marketing is a core competency of all our marketers. Umang’s role was a global position that will be not be filled. What we’re doing is recruiting a team of digital experts with specialist skills to be part of our U.S. marketing team.”
Haney’s response reflects that fact that many organizations expect CMOs to arrive hard-wired for digital, and while global corporations like Campbell Soup may have a dedicated digital team, it will operate under the stewardship of the CMO.
All of this said, the shift is far from universal. The AdWeek article goes on to cite a number of marketing experts who acknowledge that while digital is an integral part of marketing, familiarity with digital channels does not by default equate to an understanding on how to best use these channels and data for maximum impact.
Organizations seeking the right balance of internal and external digital marketing strategy and execution resources should take a handful of factors into consideration:
- Have you made significant digital marketing investments that aren’t paying off?
If you have hired digital specialists and invested in digital activities but are not seeing the expected ROI, this may be an indication that the digital initiatives lack proper strategy and innovation. There can be many reasons for this, ranging from the lack of a digital director to marketing leaders that are stretched so thin that there is no way they can devote the proper time to creating and tracking digital efforts on a day-to-day basis.
- What are the core competencies of your CMO?
CMOs bring a diverse range of skill sets, and increasingly data analytics is a competency business leaders seek to analyze the efficacy of digital marketing programs. Alternatively, some CMOs with strong data chops may not have as much experience developing innovative digital marketing campaigns that encompass video, web, social, virtual reality, etc. For organizational leaders, it’s about putting together a puzzle of personnel and capabilities that can deliver the full digital and traditional marketing strategy and execution stack that leaves no gaps.
- Can and should the CMO run the digital marketing stack?
It’s not just people and process that CMOs and digital marketing directors must run, its tools as well – digital marketing technology tools that have multiplied exponentially just in the last five years. Marketing leaders could spend a good part of their day evaluating these tools and trying to figure out the right combination for their organization based on need, budget and impact.
Marketing Land columnist Jim Yu reiterates the challenge CMOs face to navigate a web of tools that often focus too little on performance-led technology that drive a healthy ROI. Yu speaks of building digital marketing stacks that can plug gaps in the “digital performance gap,” and it is worth questioning whether all of this can and should fall to a CMO versus a dedicated digital strategist.
- How much kool aid has the marketing team been drinking?
Your marketing team may know digital, and it may know your company, but does it have a firm grasp on how competitors are marketing to target audiences? And is it up to speed on digital marketing innovation that can help the organization rise above the noise in selling products and services? While digital marketing agencies may not know your organization as well as internal staff, they can offer a gut check perspective beyond what may be possible with an internal team that is “too close” to be objective.

If Dunkin’ Donuts plasters ads on the inside of city buses, it is because they believe riders exposed to the brand – over time – will be more inclined to stop for coffee and a donut at DD rather than at Starbucks, McDonald’s, Krispy Kreme, what have you. Or even that a consumer getting on a bus not thinking about coffee or donuts will exit the bus with these items at the forefront of their consciousness.
If Dunkin’ Donuts continues with this line of thinking, they will ask themselves what else could persuade riders beyond “seeing” an ad of the brand logo and pictures of the products? Would riders be further compelled if they could “smell” the coffee or glazed donuts on the bus?
Over the past few months, we’ve been talking a lot about augmented reality marketing and virtual reality marketing – two important pieces of the sensory marketing puzzle. Effective marketing requires engaging all or many senses, however, so CMOs must identify the right multi-sensory mix to positively impact the target buyers (whether they are consumers or business users).
Sensory marketing and experiences have been around for decades and examples abound. Much of it comes down to the effects of a desensitized audience. A theme park visitor who first rides the tallest roller coaster in the world will have a thrilling experience, but what happens when the visitor rides the coaster a second, third or tenth time? So theme parks might try and activate other senses through smoke, sound, lights, etc. If you want to know where theme park attractions are headed by the way, Legoland’s new Ninjago 4-D attraction offers a hint as the first ride in North America that uses hand gestures in place of physical devices to control a ninja warrior battle. The attraction also adds sensory experiences such as heat, smoke and wind for the virtual journey.
In a recent article for Harvard Business Review, a pair of professors shared results from four studies they conducted on when sensory marketing works and when it doesn’t for brands. The studies focused on taking product brands consumers were familiar – Nokia and Apple phones – and adjusting the product and packaging to gauge impact on brand perception. Prior to showing research subjects the new phones and packaging, the researchers first determine that Apple was viewed as the “exciting” brand and Nokia the “sincere” brand. This was important, because according to the study, brand perception impacted the amount of leeway Apple and Nokia had to fundamentally alter the product, packaging, and promotional experience.
The bottom line, according to the authors, is that consumer preference can be altered by sensory marketing tactics, but how well the tactic works depends on the brand’s personality. Apple as an “exciting” brand may be able to get away with surprising consumers with unexpected sensory experiences without undoing positive brand perception, whereas Nokia may risk alienating loyal customers if radical changes run counter to its brand sincerity.
The researchers went on to conclude from the four studies that overall, individuals prefer sincere brands (hallmark, Ford, Coca-Cola) over exciting brands, “when the brand’s packaging or promotional accessories felt and looked the same, but they preferred exciting brands (Mountain Dew, BMW, Pepsi) when the brand’s packaging or promotional accessories did not feel and look the same.”
As sensory options for marketers extend from see and hear to smell, touch and immersion, a host of new opportunities open up for CMOs – opportunities that become risks if the CMO overlooks some key takeaways from these studies. Creating a virtual or augmented reality experience in and of itself will not necessarily turn off users of a sincere brand, but marketers must be mindful of risks if the experience itself does not stay true to sincerity of the brand. To learn more about the importance for VR marketing, reach out today:

I don’t know what happened with the supposed “do not call” list, but lately I’ve been bombarded with nonstop robocalls purporting to be from my credit card company. The friendly robovoice assures me right off the bat that, “there is nothing wrong with my account, I should not be alarmed, but that I’m running out of time to lower my rate…”
It’s right at that point where I disconnect the call. Brands are getting more clever (or devious) with phone marketing for sure; I’ve noticed that credit card firms now use a local area code in the caller ID, expecting that people will be more inclined to answer a call from a local unknown number than an unknown 800 number. Earlier this week, the caller ID on my mobile phone suggested that the incoming call was from none other than…myself – which feels more like the plot for Scream 5 than savvy marketing.
While phone marketing seems to be sliding down a slope to irrelevance, email marketing remains an effective tool for brands. A 2016 study by Selligent/StrongView charts that 60 percent of brands plan to increase spending on email marketing this year compared to 2015, and in a separate eConsultancy 2015 survey, nearly three-quarters of marketing teams still believe email communication will be one of the channels with the highest ROI in 2020.
While signs point to email marketing enduring in the coming years, it may not look the same as it does today. That is because a fierce battle is being waged between art and science. There is an undeniable “art” to crafting email marketing content and subject lines that grab a prospect’s attention and drives them to action. At the same time, email marketing has become a “science” driven by machine learning that draws on big data analytics beyond what any human is capable of.
Startups and emerging technology providers are increasingly betting on “science.” Persado, for example, is a self-described “cognitive content platform” that last week announced a $30 million investment led by Goldman Sachs. Persado’s software utilizes machine learning and performance information of millions of messages to help brands select optimal language for email subject lines and other campaigns. It is an approach that Persado Founder & CEO Alex Vratskides refers to as “persuasion automation.”
While Persado and similar software offerings can be an effective tool in the marketer’s toolbox, creative teams will not replaced anytime soon. Only 13% of respondents in the eConsultancy survey “strongly agree” that all email marketing will be automated by 2020, though 40% “somewhat agree” with this statement – signaling that CMOs will continue to look for the right mix of automation and human creative teams to develop and execute these programs.
Ultimately, creative teams will remain vital for not only developing email subject line language that drives desired action, but also for ensuring each program reflects and remains consistent with the brand vibe (humor, provocative, direct, etc.). This input augments, rather than replaces, the value that high performance marketing language software tools can deliver when it comes to improving conversion and ROI.
Apologies in advance if you now have the 1981 Olivia Newton-John classic stuck in your head for the rest of the day. If you live on the East Coast you have no doubt been getting “very physical” the past few days if you catch my snowdrift. After all, it’s hard work moving bottomless mounds of snow from one heap to another. What did you think I referring to? C’mon now, let’s keep it kosher.
Digital marketing became increasingly essential to consumer marketers in 2015, but there is strong evidence that digital is being elevated from just another item in the CMO toolbox to a pervasive ingredient to all marketing activities.
Exhibit A is findings from the Gartner 2015-2016 Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) Spend Survey, that focused on business leaders responsible for marketing – digital marketing in particular – across 339 large and extra-large (whatever that means) companies in North America and the U.K. A whopping 98% of CMOs consider digital marketing mainstream and that online and offline marketing are merging.
Commenting on the results, Yvonne Genovese, group vice president at Gartner, notes: “Marketers no longer make a clear distinction between offline and online marketing disciplines. As customers opt for digitally led experiences, digital marketing stops being a discrete discipline and instead becomes the context for all marketing. Digital marketing is now marketing in a digital world.”
In our marketing projects with leading consumer, business and public sector organizations, we are seeing significant demand for the “digitally led experiences” that Gartner references. There are a few digital marketing trends in particular that consumer marketers should keep their eyes on in 2016:
Smartphone ad geo-fencing
Consumer marketers recognize the need to map digital marketing into the consumer buyer’s journey when these digital assets can have the biggest impact. At what moment and location will the consumer be most inclined to play a video, read a text message or view an in-app ad? Smartphone ad geo-fencing enables marketers to reach an audience when they are most receptive to your brand, product, or service marketing.
Think about a consumer’s mindshare when entering an airport. In the traveler waiting for a flight, you have a captive audience thinking about various aspects of their business or leisure travel. Do they need accommodations, transportation, dinner reservations, or other concierge-type services? Smartphone ad geo-fencing can feed location-based ads to travelers once they enter an airport at a time when they are primed to take action.
Virtual Reality
Yeah, yeah, you’ve been hearing about virtual reality headsets for years. But VR is primed for mainstream in 2016. Oculus Rift has set an April release, in addition to other planned releases for HTC Vive and Playstation VR, are poised to put VR in the hands of consumers for hundreds – not thousands – of dollars. But the fact is that consumers don’t need to even shell out this kind of cash to experience virtual reality.
My colleague Michael Quint recently blogged about how Bluetext is leveraging Google Cardboard to bring virtual reality to the masses. Today, we are designing a digital briefing center for a client in virtual reality by marrying, in Michael’s words, “our creativity, advanced video capabilities, and cutting-edge app development to help a software company more effectively tell its story.” In this case it’s a b2b company, but we fully expect b2c virtual reality projects to become increasingly commonplace as the year progresses.
IoT
Consumer marketers are not alone in trying to get their hands around the Internet of Things, and how to leverage IoT for digital marketing efforts. In my end-of-year blog post, I looked at the IoT opportunity for digital marketers in 2016, and what it comes down to is that marketers will be able to capture a growing volume of data on consumer behavior and consumption patterns from connected devices and sensors, and then engage with consumers more effectively based on this data.
Marketing Automation
In a Forrester report, “2015: The Year of the Big Digital Shift,” more than half of marketers admitted their digital marketing is more tactical than strategic. Digital marketers are a victim of their own excess: Forrester reported that investments in marketing technology grew 3.4 percent in 2014 and is projected to rise another 4 percent this year. So consumer marketers will not lack for tools and options, but 2016 is the year when CMOs and their teams must invest time to identify the optimal set of tools to catapult their initiatives. They also most move beyond an understanding of the ‘basic’ capabilities of marketing automation tools, and shift from students to experts fully versed in the in’s and out’s of marketing automation.
The team here at Bluetext will wind 2015 down with significantly more Internet of Things (IoT) domain expertise than when the year began. Several clients are playing a key role in shaping the future of this nascent technology – one that is sure to touch more consumers, businesses and government agencies in 2016.
Digital marketers are typically not “Naughty by Nature,” but given that Gartner projects a 30 percent increase in the number of connected “things” next year, it is a safe bet that we will be down with IoT. A study conducted by 2nd Watch earlier this year found nearly six in 10 U.S. IT and business executives leveraged IoT/machine data for digital marketing, though the majority (two-thirds) acknowledged these efforts were in the initial stages.
While the Internet of Things presents a massive opportunity, tapping into it won’t be easy. Marketers, already struggling to stay afloat amidst a sea of data, will find that the exploding number of IoT sensors has them drowning in it. Sure enough, data volume is no longer the problem; it’s being able to analyze data and extract meaningful insights from it that will drive successful marketing and advertising campaigns. Capturing and analyzing this data will place an even greater premium on having the right digital marketing tools to automate as much of this process as possible.
As agencies and brands gain a handle on the data volume, look for the Internet of Things to unlock several new digital marketing opportunities in 2016.
- Use IoT for marketing to user behavior patterns – Smart home technologies such as connected thermostats and smart fridges offer marketers an opportunity to reach consumers at the right time and with the right message. Thermostats and home energy management mobile apps empower marketers to tap into a wealth of data regarding energy consumption patterns and activity patterns within the home in a way that can trigger marketing efforts around products (HVAC, filters, windows, roofing, etc.). Or consider the sensor data pushed to brands from smart fridges able to recognize the products you buy and supply levels in a way that can feed discounts and coupons at the opportune time and impact brand purchasing decisions in the process.
- Use IoT to own the buyer journey – The ability to reach target audiences more frequently and with greater personalization throughout the awareness, consideration and decision stages of the buyer’s journey positions IoT to augment traditional touch points such as offline and online advertising, social media, mobile, email, etc. For B2C, smart TVs offer brands a captive audience that can be marketed to before they conduct a product search via Google or in person at the store. For B2B, the ability for technology vendors to understand when printers need to be replaced or cartridges refilled, when warehouse suppliers are running or when businesses are not using energy efficiently can accelerate the buyer journey.
- Use IoT to pull and push data – At this point in its evolutionary cycle, the great value of IoT is that digital marketers can access real-time information on how business users and consumers use products, when they use them, and what motivates them to do so. 2016 will see the early stages of the digital marketer use case shift from pulling all this data to then using analytics to push information back.
- Track where wearables are headed – Try saying that five times really fast. Wearables may be among the most hyped aspects of the Internet of Things, and the market trajectory remains uncertain. The Apple Watch sparked a great deal of imagination pre-launch, and as 2015 comes to a close the technology giant – and its customers – are still feeling their way on how these devices can best be used. Internet connected wearables are poised to extend far beyond just watches; from clothing and shoes to augmented reality devices there exists an opportunity for brands and agencies to reach audiences beyond smartphones and tablets.
- Cars may be ground zero for IoT – Americans drive more than 29 miles per day, making two trips at an average duration of 46 minutes. Those really depressing figures come courtesy of a 2015 study by the AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety and the Urban Institute. For commuters, these numbers are tough to swallow; but for digital marketers identifying the best places to reach target audiences, they are numbers that cannot be ignored. Vehicles are more connected than ever through software systems, and as the vehicle becomes just another data collecting sensor on the move, advertisers and marketers gain valuable insights into when and where people go. The in-vehicle ads become more targeted and valuable, and brands can literally change the course of vehicle destinations based on consumer data.
To learn more about the possibilities IoT offers, contact Bluetext today:
Back in 2006, I had a conversation with Washington Post Magazine columnist Gene Weingarten, one of my favorite humorists. If you’ve ever happened upon his column, you know that he’s not exactly an admirer of public relations professionals or publicists. So I made him an offer: let’s switch jobs for a day. I’ll write your column for one week while you handle all my PR clients. Gene thought about it for a bit, and then said yes…with a catch. He’d only do it if I would admit, on the record in his column, how pathetic and meaningless my existence as a PR professional was. Intriguing offer, but ultimately I passed. Then I went home, grabbed a bottle of Jack Daniels, shut the closet door, and cried.
Ok, so I’m kidding the last part. I don’t actually own a closet. I’m not sure why the exchange with Gene recently popped into my head, but perhaps it results from what seems to be a Groundhog Day cycle of working with traditional DC tech press, which goes something like this: Establish relationship with DC tech reporter, work with reporter on multiple client stories, watch reporter leave publication after relatively short period of time (typically right at the moment when I have 2-3 stories on precipice of publication), bang head into wall, dream about being a farmer, realize I wouldn’t survive six hours on a real farm with live animals, start process all over again with replacement, and hope springs eternal.
Washington Business Journal tech reporter Kasra Kangarloo is the most recent area tech reporter to leave the position, a beat he held for less than 8 months. Actually, I spoke to soon; Washington Post reporter Amrita Jayakumar (who covered tech as part of a broader beat) departed a few weeks after Kasra. Preceding these tech scribes were Bill Flook at WBJ and Steven Overly at the Post. All four were good writers and good individuals who invested time to get to know the tech community – which is all you can ask for.
Editorial churn is not unique to this market, and there is no need to run through the upheaval occurring with traditional publishing. But one has to assume that the revolving door partially derives from the fact that these writers did not feel the position was stimulating or rewarding (financially or professionally). Traditional publishers in this market have been de-prioritizing local tech coverage due to a range of factors. This begs the question of whether it matters – not just for individual tech companies seeking to generate awareness for their brand, products and services – but for the DC tech community as a whole.
While most of these reporters transitioned quietly to their next professional stop, Kangarloo hopped out with somewhat of a bang. It wasn’t an exit on par with George Costanza scraping up New York Yankees championship trophies as he spun his car around the parking lot, but it did capture the attention of the DC tech community. Kangarloo led off his exit post stating, “Fare thee well, D.C. tech. It’s been real.” In fact, Kangarloo didn’t think it had been real at all:
“Obviously, it’s in every startup’s interest to drum up positive press, and there is a genuine financial incentive for any one of them to, shall we say, bend the truth a bit. And since I’m leaving the beat for good, I’ll just go ahead and say what I really mean by that — the startup realm seems to rival even political coverage for the sheer amount of spin that’s employed each day. But why so many reporters give in so easily is a mystery. And that’s not to exclude myself, by the way. I’ve fallen into that trap plenty of times, and had I stayed longer I’m certain I would again.”
If a startup announces a major new customer and no one is around to write about it, did it happen? If the next set of tech reporters at WBJ and the Post cast an equally cynical eye towards the DC tech community, does that impact the ability for startups and others to get important stories out? I can understand, as a reporter, that it is far more fulfilling to dig into more controversial, investigative pieces than it is to regurgitate funding announcements or hearing a founder wax on about some grandiose vision to change the world…or supply chain efficiency as the case may be. And investigative stories should be told. But so should stories of startup and tech success.
The good news for DC is that the next generational of editorial players, including DC Inno, Tech Cocktail (yes, have been around for a while), Technical.ly DC, Tech Bisnow and even the DC Tech Facebook page, have stepped in to fill the gap. They’ve also served notice, for the most part, that they aren’t satisfied to just repost press releases.
For DC starts and other tech firms, all of this change means a couple of things – none of it revolutionary. First, proximity matters, and startups and tech innovators may have to leave their comfort zone, metaphorically and geographically speaking, to find the outlets that matter most to them. It may be TechCrunch, it may be The Wall Street Journal, but it could just as likely be Builder Magazine or Hotel Business. Because as many layoffs or job switches that might be occurring across the industry, you will find greater stability at influential outlets outside of the market (TechCrunch, Re/Code, The Next Web, QZ, etc.), where some writers have been there for years, not months. This stability is important, because reporters get to know a company and don’t need to be re-educated on a continuous basis.
Second, think about how traditional and emerging DC tech writers want to cover the space. Don’t just email a press release about what a new product does, connect them with a customer who can provide tangible ROI evidence your product makes a difference. If your funding announcement is not a big number – relatively speaking – connect the funding to a broader local or national trend that expands the story beyond your own. The press release isn’t a news generator; it’s simply an SEO information capsule representing one small part of your announcement strategy.
If Jon Favreau’s character in Swingers met sponsored content at a bar a few years back and snagged its phone number, he might pin the number up on his calendar, but he would never call her. Ever. Because sponsored content lacked brains, beauty and charm.
But sponsored content – and content marketing in general for that matter – has come a long way from its origins as glorified and often ineffective native advertising. Today, Vince Vaughn’s character would take a look at sponsored content, hop up on the table, swing his shirt around and yell, “You know what big boy? You’re grown up. Cuz you’re growns up and you’re growns up and your growns up!”
While Vaughn’s sentiments will have once again obliterated the English language, his point would be well taken. Sponsored content has “growns up.” Publishers are taking sponsored content very seriously because it has become key to their financial lifeblood. Desperation leads to innovation, and experimentation – all good news for brands reluctant to part with traditional advertising dollars but that increasingly view mature sponsored content opportunities as a way to reach and influence target audiences.
In a recent interview, AOL Inc. CMO Allie Kline reaffirmed its view that content marketing is not advertising. While some of the campaigns she references stretch the limits of how we define content marketing, that is kind of the point; the definition is changing as the data, distribution and content becomes more sophisticated.
Sponsored content is one component of content marketing. Sometimes it is easily identifiable, while in other cases the sponsored content is cloaked within traditional editorial content. The latter development is a testament to the fact that display ads and other overt forms of online advertising are falling out of favor, and brands increasingly seek a way to have their content woven into earned editorial content, where it is less obvious to the reader, viewer, listener that the content is in fact “sponsored.” When was the last time you clicked on a banner ad? For me, it only happens when the web page I’m viewing shifts unexpectedly at the last second and causes me to click on an ad rather than the editorial content I actually wanted to read.
In our work with clients, we’ve been increasingly evaluating and making recommendations on sponsored content for technology brands. Based on this work, there are a few considerations brands should keep in mind when embarking on a sponsored content program.
Publishers are upping their game
Traditional publishers are no longer ceding the curated content game to agencies and other players in the market. Look no further than The Guardian, a well-known global publication that in 2014 launched Guardian Labs, an in-house branded content agency. Brands such as Silence Circle, a hot encrypted communications firm, chose Guardian Labs this year for a sponsored content program to promote the company. It is reported that Guardian Labs has 133 staff members, and there is no doubt that other publications will be closely watching efforts such as these to gauge whether they can launch similar efforts.
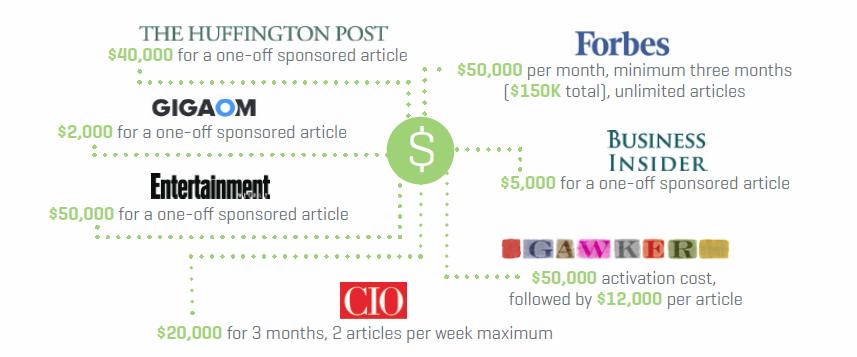
Similarly, QZ.com, an up-and-coming news and tech site, has teams of content, video and design experts working with brands such as HP on this infographic-anchored sponsored content, to build high impact sponsored content that will grab the reader’s attention. So what brands see today is a far cry from advertising and the full page “advertorials” that had an editorial flavor to them, but were still noticeably out of sync with a publication’s earned editorial content.
The details are in the fine print
TechCrunch, Forbes, Re/Code, CIO.com, you name the technology out let and most likely there will be a sponsored content option. Before selecting one or more outlets to work with, the brand should get answers to several key questions:
- Where will the sponsored content post direct the target? Some technology outlets will redirect users clicking on the sponsored content teaser to content that resides on the outlet’s site and looks and feels similar to earned editorial content on the site. The benefits to this approach
- What type of sponsored content works best? Sponsored content can, in theory, be self-promotional about a company or product, or it can be more traditional thought leadership whereby the goal is to attach the brand to a vision or market trend. While one could argue that self-promotional content can more directly link the target to a buying action, doing so makes the sponsored content more “ad” like relative to thought leadership content.
- What happens to the sponsored content post? A typical sponsored content scenario is that the teaser will appear in a vertical scroll within the top 10 news stories on a technology site. Brands must understand how long the content sits in that position, what happens to the content after it leaves the prime position and is shifted to another part of the site, and whether this content leads to another part of a site or an external landing page the brand (or publisher) most construct for this campaign. In some cases, a sponsored content piece might only run in prime position for one day, so understanding where the content travels to from there is key.
- Do they use CPM or fixed-fee model? In some cases, editorial outlets will use the ‘cost per thousand impressions’ fee structure, while in others it is a set fee determined by the publisher based on a broad range of factors. Each model has pro’s and con’s that should be evaluated.
Do listicles work for b2b brands?
List + Art (icles), otherwise known as listicles, have exploded on the b2c side of the house. Scroll through Yahoo News or any other consumer content site and you are bound to bump into some inane list along the lines of “Top 5 ways to pay off your mortgage,” “The 8 best places to eat fried chicken without a napkin,” or “Top 10 reasons you shouldn’t eat scallops.” How much these listicles contribute to society is debatable, but the listicles are eminently clickable and work reasonably well. For B2B sponsored content however, listicles remain a work in progress and must have a more substantive theme and valuable content that relates to the user’s pain points.
Does sponsored content work?
In January of this year, a blog post by SEO firm Moz did a fantastic job of analyzing the current state of sponsored content, and the potential for brands to see stronger results relative to advertising. In its “Content Promotion Manifesto,” Moz estimated that brands spent, on average, 6.7 percent of their content marketing budgets on sponsored content in 2013– and surely that figure has increased measurable since then.
In terms of effectiveness, the Moz blog post also cites a Contently survey of Internet users that reveals brands have a real opportunity to influence decision makers with sponsored content. Nearly half (48%) of respondents believe sponsored content that was labeled as such was paid for by an advertiser that influenced the content produced. The majority felt the “sponsored content” label meant something else.
Equally encouraging is that the survey finds one-third of respondents are as likely to click on a sponsored article as they are to click on unsponsored editorial content. The Moz article also references a separate study that actually found consumers look more at sponsored articles (26%) than typical earned editorial articles (24%). Publishers have seized on the strong results and favorable consumer/business user data, charging brands five and six figure amounts for individual and limited-run campaigns (as the Moz chart below indicates).
The bottom line for brands evaluating sponsored content is to build a clear set of goals and objectives for the campaign, and identify the right partners to execute it.
When it comes to where a brand should spend its video ad dollars, YouTube has long been the go-to destination. With more than 3 billion video views per day, content producers direct the majority of its efforts here – and unsurprisingly the advertiser budgets have followed.
But this presumption is being seriously tested by a video traffic explosion – chronicled in great detail by Fortune magazine writer Erin Griffith – underway at Facebook. Facebook users are watching 4 billion video streams a day, which is a 4x jump from just twelve months ago. Granted, Facebook counts a “view” as any video that plays for three seconds, which means that users scrolling down their feed and allowing a video to briefly auto play before moving on inflates the view total. Nonetheless, 4 billion is 4 billion.
Fortune’s Griffith goes into some of the reasons behind social network’s video success – which unsurprisingly includes efforts by engineers to adjust algorithms that make it not only easier to watch videos, but also to share them. While Griffith’s focus is on how all of this impacts advertisers and where they spend their money, Facebook’s rapidly growing impact with video presents a conundrum for B2B and B2G brands and the public relations/marketing firms that represent them.
In evaluating the major social networks and where to focus resources, investment and, most importantly, content, Facebook typically comes up last for firms seeking to influencer decision makers across government and businesses. Sure, everyone is on Facebook, so it goes, but the working assumption is that the largest social network is where you go to view new pics of the grandkids or post updates from the beach – not to consume B2B/B2G focused content.
Griffith’s article supports as much when it comes to videos, with the author pointing out that, “…Facebook’s biggest advantage over YouTube and other video providers may be boredom.” Griffith suggests someone lands on a YouTube video either because they are searching directly for it or a related topic, or a video being shared is ultimately sourced on that site. With Facebook, most of the time we are watching videos because we are killing time on the site and it is just another thing to do.
Because Bluetext works with so many B2G and B2B firms, social media strategy comes up quite a bit. Often, recommendations lean towards LinkedIn, Twitter and YouTube depending on the ultimate goal and category of decision makers the client is trying to reach. Even with B2B and B2G clients for whom we are not supporting social media, Facebook is usually trailing the pack in their social efforts.
But the fact is that Facebook drives one-quarter of all web traffic, and its video traffic explosion demands B2B and B2G firms reevaluate how best to use the site with video content. Is it ideal for placing corporate marketing, event or deeply technical product and service videos? No, absolutely not. But are there times when Facebook, rather than YouTube, should be ground zero for launching a more consumable brand humor video or engaging content that can be easily viewed – and shared – across Facebook and then on to other destinations? 4 billion video streams a day say yes, and going forward B2B and B2G brands may be saying yes as well.
The majority of Bluetext public relations engagements are ongoing retainers with clients looking for long-term, strategic PR support – whether it is a client transitioning from a former PR agency or engaging with an outside agency for the first time.
But from time to time, our public relations work revolves around a single project. It could be a startup seeking to maximize coverage of a venture capital funding round announcement, a technology company establishing a presence in a new country or geographic region, or other scenarios of that ilk. What’s great is that sometimes those one-time projects become something more, and even if they don’t, the experience is almost always a rewarding one.
The Bluetext team recently completed a PR project different than most: the client, Galois, was set to be featured in an upcoming national TV news segment, and it wanted to maximize and build upon this lightning-in-a-bottle opportunity.
First, a little background on Galois: Founded in 1999, Galois applies cutting edge computer science and mathematics to solve difficult technological problems for military and commercial organizations. Galois produced a software programming language that made drones and UAVs invulnerable to attack. As importantly, the technology was developed to be applicable to prevent hacking of control systems in air and ground vehicles such as the increasingly connected modern automobile.
What made the project rewarding for Bluetext is the passion that oozed from everyone at the organization – from the CEO on down. To be able to work with individuals who are committed to improving security at the citizen, enterprise and national defense level inspires our team to do great work.
The national TV segment ran in February 2015, and though Galois’ part – as is often the case – was narrowed for time purposes, it remained a great opportunity to share Galois work with its target audiences – government, military, contractors, enterprise.
Bluetext pushed ahead with a strategic plan built around converging interest, policy developments and public awareness of security vulnerabilities associated with Drones, UAVs, modern automobiles and commercial aircrafts. Bluetext worked with Galois executives and subject matter experts to develop high impact pitches, a press release, and access to third party, credible researchers that could validate the importance of Galois’ work.
In addition to interviews arranged with CNN, CNBC, USA Today and The Washington Post, coverage was also secured in numerous publications listed below over a compact, six-week period:
Drone magazine — http://www.dronemagazine.net/drones/software/galois-develops-anti-hacking-software-for-commercial-uavs
GCN — http://gcn.com/articles/2015/03/17/secure-drone-software.aspx
The Washington Post – http://www.washingtonpost.com/business/on-it/can-you-vote-for-the-next-president-on-your-smartphone-not-just-yet/2015/04/04/8028a174-d715-11e4-8103-fa84725dbf9d_story.html
NextGov — http://www.nextgov.com/cybersecurity/2015/03/pentagon-path-launch-hacker-proof-boeing-drone-2018/107250/
DefenseOne — http://www.defenseone.com/technology/2015/03/pentagon-launch-hacker-proof-helicopter-drone-2018/107355/
EnGadget — http://www.engadget.com/2015/03/16/pentagon-wants-unhackable-helicopters/
ExecutiveBiz — http://blog.executivebiz.com/2015/03/boeing-built-unmanned-aircraft-set-for-flight-in-2017-john-launchbury-lee-pike-comment/
Unmanned Aerial — http://www.unmanned-aerial.com/e107_plugins/content/content.php?content.970#.VQwjlGTF_0o
UAS Magazine — http://www.uasmagazine.com/articles/1029/galois-develops-software-tools-to-make-better-uas-systems
Bend Bulletin – http://www.dailyherald.com/article/20150411/business/150419974/
Chicago Daily Herald — http://www.dailyherald.com/article/20150411/business/150419974/
Tactical is a great word…if you are in law enforcement or the military. As a digital marketer, however, tactical has come to imply – fairly or unfairly – a lack of strategy, creativity and inability to grasp how day-to-day activities fit into the bigger picture.
In the recent Forrester report, “2015: The Year of the Big Digital Shift,” more than half of marketers admitted their digital marketing is more tactical than strategic. While a number of factors may explain this, digital marketers are a victim of their own excess: Forrester reported that investments in marketing technology grew 3.4 percent in 2014 and is projected to rise another 4 percent this year.
Marketers looking to spend their growing budgets will find an ever-expanding landscape of digital marketing tools at their disposal. Ask peers for recommendations on tools for content marketing, marketing automation, mobile marketing, SEO, and social media monitoring and you will likely get dozens of answers. It reminds me of the viral marketing videos from Blendtec’s, “Will It Blend” campaign, whereby items ranging from iPhones to baseballs are placed in a Blendtec blender to see if, in fact, they will blend. Throwing a bunch of digital marketing tools into a blender and just hoping they will “blend” together into a coherent strategy doesn’t work.
To ensure digital tools enhance rather than complicate your broader marketing strategy, consider the following:
Conduct gap analysis
Marketers must draw a definitive line between nice to have and need to have digital tools. In my recent column for PR Week The Hub Comms, I reviewed a new gap analysis tool from SAP that asks the marketer a series of questions about their organizational profile, marketing programs, current systems and processes. Based on the answers, the tool makes personalized recommendations on focus areas for marketing investment to address existing gaps. Marketers should not make tool investment decisions before having a firm grasp of existing gaps, and then evaluating which tools can plug them.
Avoid tool redundancy
There are purpose-built digital marketing tools designed to address a single pain point, such as SEO or content marketing. But it is more common today to find tools that try and do multiple things. For example, one tool might be capable of social media management, PR media measurement and reporting, while another might include a PR media database and some social media management capabilities. Many of these tools don’t run cheap, which means you do not want to be paying multiple vendors for essentially the same service.
Don’t repeat the same mistakes
The path of least resistance is continuing to use the same tools year after year. It is certainly possible that a small handful prove invaluable and are worthy of your loyalty, but the fact is that marketing needs evolve over time and your marketing strategy must adapt accordingly. The key point is that your digital marketing strategy should drive the tools you use, not vice versa. Purchasing a tool or tools and then building a marketing strategy around the tool’s capabilities is a backwards approach that will leady to tactical, rather than strategic decisions. Evaluate what worked last year and evaluate tools that will help you achieve objectives in 2015.
Don’t buy tools in a vacuum
Marketers, particularly those in the technology industry, often talk about how their company or client solutions break down silos and allow for information to be more easily shared. We see that playing out across agencies as far as a need to integrate digital marketing tools with other areas of the business. Burson-Marsteller recently unveiled a new approach aiming to combine its data analytics and Web data tools with creative and production capabilities, indicative of efforts industry-wide to cast the benefits of analysis, data and measurement organization-wide.